Portuguese people
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Portuguese: Portugueses, Portuguesas | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Total population | |
| Portugal: c. 10.6 million[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| c. 5,000,000 (includes Portuguese nationals and their descendants down to the third generation; excludes more distant ancestry)[2] | |
| 2,000,000 (Portuguese born & ancestry)[3][4][5] | |
| 1,400,000 (Portuguese ancestry)[6][7][8] | |
| 1,300,000 (ancestry)[9][10] (additional 55,441 Portuguese born)[11][12][13] | |
| 550,000 (Portuguese ancestry)[14][15][16][17] | |
| 500,000[18] | |
| 460,173[19][20][21] | |
| 244,217[22] | |
| 200,000 (42,008 citizens)[23][24] | |
| 200,000[25] | |
| 184,774[26] | |
| 170,000[27][28] [21][29][30][31] | |
| 152,616[32] | |
| 151,028[33] | |
| 100,000 (Bayingyi)[34][35] | |
| 80,654[36] | |
| 80,000[37][38] | |
| 73,903[39][40] | |
| 42,000[41][42][43][44][45] | |
| 40,000 (Burgher)[46] | |
| 40,000 (Kristang)[47][48][49][50] | |
| 35,633[51] | |
| 22,318 (ancestry)[4] | |
| 20,853[52] | |
| 20,700[53][54] | |
| 19,000[55] | |
| 18,000[56] | |
| 17,000[57][58][59] | |
| 16,308[60][61] | |
| 16,000 (ancestry)[62] (1,643 Portuguese born)[11][63] [64][65][66][67][68] | |
| 15,000[69][70][71][72] | |
| 10,400[73] | |
| 9,542[74] | |
| 9,000 [75] | |
| 8,288[76][77] | |
| 7,971[78] | |
| 7,245[79][80] | |
| 6,400[81] | |
| 5,700[82] | |
| 5,700[83] | |
| 4,945[84] | |
| Languages | |
| Portuguese | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Roman Catholic[85][86] | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Romance-speaking peoples Especially Galicians, Spaniards, and other Lusophones | |
^a Total number of ethnic Portuguese varies wildly based on the definition. | |
The Portuguese people (Portuguese: Portugueses – masculine – or Portuguesas) are a Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation indigenous to Portugal, a country in the west of the Iberian Peninsula in the south-west of Europe, who share a common culture, ancestry and language.[87][88][89]
The political origin of the Portuguese state can be traced back to the founding of the County of Portugal in 868. However, it was not until the Battle of São Mamede (1128) that Portugal gained international recognition as a kingdom through the Treaty of Zamora and the papal bull Manifestis Probatum. This establishment of the Portuguese state in the 12th century paved the way for the Portuguese people to unite as a nation.[90][91][92]
The Portuguese played an important role in sailing, and explored several distant lands previously unknown to Europeans in the Americas, Africa, Asia and Oceania (southwest Pacific Ocean). In 1415, with the conquest of Ceuta, the Portuguese began to play a significant role in the Age of Discovery, which culminated in a colonial empire, considered as one of the first global empires and one of the world's major economic, political and military powers in the 15th and 16th centuries, with territories that are now part of numerous countries.[93][94][95] Portugal helped to the subsequent domination of Western civilization by other neighboring European nations.[96][97][98][95]
Due to the large historical extent from the 16th century of the Portuguese Empire and the subsequent colonization of territories in Asia, Africa and the Americas, as well as historical and recent emigration, Portuguese dispersed to different parts of the world.[99]
Ancestry
[edit]The Portuguese people's heritage largely derives from the Indo-European (Lusitanians, Conii)[100][101][102] and Celtic peoples (Gallaecians, Turduli and Celtici),[103][104][105] who were later Romanized after the conquest of the region by the ancient Romans.[106][107][108] As a result of Roman colonization, the Portuguese language – the native language of the overwhelming majority of Portuguese people – stems from Vulgar Latin.[109]
A number of male lineages descend from Germanic tribes who arrived as ruling elites after the Roman period, starting in 409.[110] These included the Suebi, Buri, Hasdingi Vandals and Visigoths. The pastoral North Caucasus' Alans left small traces in a few central-southern areas (e.g. Alenquer, from "Alen Kerke" or "Temple of the Alans").[111][112][113][114]
The Umayyad conquest of Iberia, between the early 8th century until the 12th century, also left small Moorish, Jewish and Saqaliba genetic contributions in the country.[115][116][106][107][117] Other minor – as well as later – influences include small Viking settlements between the 9th and 11th centuries, made by Norsemen who raided coastal areas mainly in the northern regions of Douro and Minho.[118][119][120][121] There is also low-incidence, pre-Roman influence from ancient Phoenicians and Greeks in southern coastal areas.[122]
Name
[edit]The name Portugal, from which the Portuguese take their name, is a compound name that comes from the Latin word Portus (meaning port) and a second word Cale, whose meaning and origin are unclear. Cale is probably a reminder of the Gallaeci (also known as Callaeci), a Celtic tribe that lived in the area today part of Northern Portugal.
There is also the possibility that the name comes from the early settlement of Cale (today's Gaia), situated on the mouth of the Douro River on the Atlantic coast (Portus Cale). The name Cale seems to come from the Celts – perhaps from one of their specifications, Cailleach – but which, in everyday life, was synonymous with shelter, anchorage or door.[123] Among other theories, some suggest that Cale may stem from the Greek word for "beautiful" kalós. Another theory for Portugal postulates a French derivation, Portus Gallus[124] "port of the Gauls".
During the Middle Ages, the area around Cale became known through the Visigoths as Portucale. Portucale could have evolved in the 7th and 8th centuries, to become Portugale, or Portugal, from the 9th century. The term denoted the area between the Douro and Minho rivers.[125]
Early inhabitants
[edit]The early populations
[edit]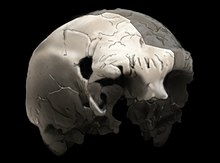
The Portuguese are a Southwestern European population, with origins predominantly from Southern and Western Europe. The earliest modern humans inhabiting Portugal are believed to have been Paleolithic peoples that may have arrived in the Iberian Peninsula as early as 35,000 to 40,000 years ago. Current interpretation of Y-chromosome and mtDNA data suggests that modern-day Portuguese trace a proportion of these lineages to the paleolithic peoples who began settling the European continent between the end of the last glaciation around 45,000 years ago.
Northern Iberia is believed to have been a major Ice age refuge from which Paleolithic humans later colonized Europe. Migrations from what is now northern Iberia during the Paleolithic and Mesolithic link modern Iberians to the populations of much of Western Europe, and particularly the British Isles and Atlantic Europe.[126]
Y-chromosome haplogroup R1b is the most common haplogroup in practically all of the Iberian peninsula and western Europe.[127] Within the R1b haplogroup there are modal haplotypes. One of the best-characterized of these haplotypes is the Atlantic Modal Haplotype (AMH). This haplotype reaches the highest frequencies in the Iberian Peninsula and in the British Isles. In Portugal it reckons generally 65% in the South summing 87% northwards, and in some regions 96%.[128]
The Neolithic
[edit]The Neolithic colonization of Europe from Western Asia and the Middle East, beginning around 10,000 years ago, reached Iberia as well as it had previously reached the rest of the continent, although according to the demic diffusion model its impact was greatest in the southern and eastern regions of the European continent.[129]
The Celts and the arrival of the Indo-Europeans
[edit]
Starting in the 3rd millennium BC, during the Bronze Age, the first wave of migrations by speakers of Indo-European languages into Iberia occurred. Major genetic studies, carried out since 2015, have now shown that the expansion of haplogroup R1b in Western Europe, most common in many areas of Atlantic Europe, is primarily due to massive migrations from the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Eastern Europe during the Bronze Age, along with carriers of Indo-European languages like proto-Celtic and proto-Italic. Unlike older studies on uniparental markers, large amounts of autosomal DNA were analyzed in addition to paternal Y-DNA. An autosomal component was detected in modern Europeans which was not present in the Neolithic or Mesolithic, and which entered into Europe with paternal lineages R1b and R1a, as well as the Indo-European languages.[130][131][132]
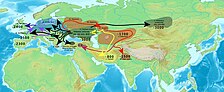
The first immigrations of Indo-European languages speakers were later followed by waves of Celts. The Celts arrived in the territory that is today Portugal about 3,000 years ago[133] even though the migration phenomenon was particularly intense from the 7th to the 5th centuries BC.[134][135]
These two processes defined Iberia's, and Portugal's, cultural landscape "Continental in the northwest and Mediterranean towards the southeast", as historian José Mattoso describes it.[136]
The northwest–southeast cultural shift also shows in genetic differences: based on 2016 findings,[137] haplogroup H, a cluster that is nested within the haplogroup R category, is more prevalent along the Atlantic façade, including the Cantabrian Coast and Portugal. It displays the highest frequency in Galicia (northwestern corner of Iberia). The frequency of haplogroup H shows a decreasing trend from the Atlantic façade toward the Mediterranean regions.
This finding adds strong evidence where Galicia and Northern Portugal was found to be a cul-de-sac population, a kind of European edge for a major ancient central European migration. Therefore, there is an interesting pattern of genetic continuity existing along the Cantabria coast and Portugal, a pattern that has been observed previously when minor sub-clades of the mtDNA phylogeny were examined.[138]
Given the origins from Paleolithic and Neolithic settlers, as well as Bronze Age and Iron Age Indo-European migrations, one can say that the Portuguese ethnic origin is mainly a mixture of pre-Celts or para-Celts, such as the Lusitanians[139] of Lusitania, and Celtic peoples such as Gallaeci of Gallaecia, the Celtici[140] and the Cynetes[141] of Alentejo and the Algarve.
Pre-Roman populations
[edit]Lusitanians
[edit]The Lusitanians (or Lusitānus – singular – Lusitani – plural – in Latin) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the Western Iberian Peninsula long before it became the Roman province of Lusitania (modern Portugal, Extremadura and a small part of Salamanca). They spoke the Lusitanian language, of which only a few short written fragments survive. Most Portuguese consider the Lusitanians as their ancestors, although the northern regions (Minho, Douro, Trás-os-Montes) identify more with the Gallaecians. Prominent modern linguists such as Ellis Evans believe that Gallaecian-Lusitanian was one language (thus not separate languages) of the "p" Celtic variant.[142][143] They were a large tribe that lived between the rivers Douro and Tagus.
It has been hypothesized that the Lusitanians may have originated in the Alps and settled in the region in the 6th century BC. Some modern scholars like Dáithí Ó hÓgáin consider them to be indigenous[144] of the country. He also claims they were initially dominated by the Celts, before gaining full independence from them. The Romanian archaeologist Scarlat Lambrino, active in Portugal for many years, proposed that they were originally a tribal Celtic group, related to the Lusones.[145]
The first area settled by the Lusitanians was probably the Douro Valley and the region of Beira Alta; they subsequently moved south, and expanded on both sides of the Tagus river, before being conquered by the Romans.
The Lusitanian ethnogenesis and, in particular, their language, is still not completely understood. They originated from either Proto-Celtic or Proto-Italic populations who spread from Central Europe into western Europe after new Yamnaya migrations into the Danube Valley, while Proto-Germanic and Proto-Balto-Slavic may have developed east of the Carpathian Mountains, in present-day Ukraine, moving north and spreading with the Corded Ware culture in Middle Europe (third millennium BCE). One theory postulates that a European branch of Indo-European dialects, termed "North-west Indo-European" and associated with the Bell Beaker culture, may have been ancestral to not only Celtic and Italic, but also to Germanic and Balto-Slavic.[146]
The Celtic root of the Lusitanians and their language, is further emphasized by recent research by the Max Planck Institute on the origins of Indo-European languages. This comprehensive genetic-linguistic study, identifies one common Celtic branch of peoples and languages spanning most of Atlantic Europe, including Lusitania, at around 7,000 BC. This new work contradicts previous theories which excluded Lusitanian from the Celtic linguistic family.[147]
In Roman times, the original Roman province of Lusitania was extended north of the areas occupied by the Lusitanians to include the territories of Asturias and Gallaecia but these were soon ceded to the jurisdiction of the Provincia Tarraconensis in the north, while the south remained the Provincia Lusitania et Vettones. After this, Lusitania's northern border was along the Douro river, while its eastern border passed through Salmantica and Caesarobriga to the Anas (Guadiana) river.
Other Pre-Roman groups (excluding Lusitanians)
[edit]
As the Lusitanians fought fiercely against the Romans for independence, the name Lusitania was adopted by the Gallaeci, tribes living north of the Douro, and other closely surrounding tribes, eventually spreading as a label to all the nearby peoples fighting Roman rule in the west of Iberia. It was for this reason that the Romans came to name their original province in the area, that initially covered the entire western side of the Iberian peninsula, Lusitania.
Here is a list of the tribes, often known by their Latin names, who were living in the area of modern Portugal prior to Roman rule:
- Bardili (Turduli) – living in the Setúbal peninsula;
- Bracari – living between the rivers Tâmega and Cávado, in the area of the modern city of Braga;
- Callaici – living along and north of the Douro;
- Celtici – Celts living in Alentejo;
- Coelerni – living in the mountains between the rivers Tua and Sabor;
- Cynetes or Conii – living in the Algarve and the south of Alentejo;
- Equaesi – living in the most mountainous region of modern Portugal;
- Grovii – a mysterious tribe living in the Minho valley;
- Interamici – living in Trás-os-Montes and in the border areas with Galicia and León (in modern Spain);
- Leuni – living between the rivers Lima and Minho;
- Luanqui – living between the rivers Tâmega and Tua;
- Limici – living in the swamps of the river Lima, on the border between Portugal and Galicia;
- Narbasi – living in the north of modern Portugal (interior) and nearby area of southern Galicia;
- Nemetati – living north of the Douro Valley in the area of Mondim;
- Oestriminis also referred to as Sefes and supposedly linked to the Cempsii.[148] There is not a consensus regarding their exact origins and location. They are believed to have been the first known humans to inhabit the whole Atlantic margin covering Portugal and Galicia, the people from ‘Finis terrae’ at the end of the Western world.[149][150]
- Paesuri – a dependent tribe of the Lusitanians, living between the rivers Douro and Vouga;
- Quaquerni – living in the mountains at the mouths of rivers Cávado and Tâmega;
- Seurbi – living between the rivers Cávado and Lima (or even reaching the river Minho);
- Tamagani – from the area of Chaves, near the river Tâmega;
- Tapoli – another dependent tribe of the Lusitanians, living north of the river Tagus, on the border between modern Portugal and Spain;
- Turdetani – In southern municipalities such as São Brás de Alportel
- Turduli – in the east of Alentejo (Guadiana Valley);
- Turduli Veteres – literally "ancient Turduli", living south of the estuary of the river Douro;
- Turdulorum Oppida – Turduli living in the Portuguese region of Estremadura and Beira Litoral;
- Turodi – living in Trás-os-Montes and bordering areas of Galicia;
- Vettones – living in the eastern border areas of Portugal, and in Spanish provinces of Ávila and Salamanca, as well as parts of Zamora, Toledo and Cáceres;
- Zoelae – living in the mountains of Serra da Nogueira, Sanabria and Culebra, up to the mountains of Mogadouro in northern Portugal and adjacent areas of Galicia.
Romanization
[edit]
The Roman Republic conquered the Iberian Peninsula during the 2nd and 1st centuries B.C. from the vast maritime empire of Carthage during the Punic Wars.
Since 193 B.C., the Lusitanians had been fighting Rome and its expansion into the peninsula following the defeat and occupation of Carthage in North Africa. They defended themselves bravely for years, causing the Roman invaders serious defeats although, in the end they were severely punished by Praetor Servius Galba in 150 B.C. Springing a clever trap, he killed 9,000 Lusitanians and later sold 20,000 more as slaves further northeast in the newly conquered Roman provinces in Gaul (modern France).
Three years later (147 B.C.), Viriathus became the leader of the Lusitanians and severely damaged the Roman rule in Lusitania and beyond. He commanded a confederation of Celtic tribes[152] and prevented the Roman expansion through guerrilla warfare. In 139 B.C. Viriathus was betrayed and killed in his sleep by his companions (who had been sent as emissaries to the Romans), Audax, Ditalcus and Minurus, bribed by Marcus Popillius Laenas. However, when Audax, Ditalcus and Minurus returned to receive their reward by the Romans, the Consul Quintus Servilius Caepio ordered their execution, declaring that "Rome does not pay traitors".
Viriathus[154] is the first ‘national hero’ and he has, for the Portuguese, the same significance that Vercingetorix[155] has for the French or Boudicca[156] enjoys among the English. After Viriathus' rule, the celticized Lusitanians became largely romanized, adopting Roman culture and the Latin language.
The inhabitants of the Lusitanian cities, in a manner similar to those of the rest of the Roman-Iberian peninsula, eventually gained the status of "Citizens of Rome". During the last centuries of the Roman colonization many saints venerated by the Catholic church emerged from the territory of modern-day Portugal. These include Saint Engrácia, Saint Quitéria and Saint Marina of Aguas Santas among others.
The Romans also left a major impact on the population, both genetically and in Portuguese culture; the Portuguese language derives mostly from Latin, given that the language itself is mostly a local later evolution of the Roman language after the fall of the Western Roman Empire.[106][107] According to Mario Pei, the phonetic distance found nowadays between Portuguese and Latin stands at 31%.[157][158] The Roman domination lasted from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD.
Middle Ages
[edit]
After the Romans, Germanic peoples, namely the Suebi, (see Suebi Kingdom) the Buri, and the Visigoths (who are estimated to have formed 2–3% of the population),[160][161][162][163] ruled the peninsula as elites for several centuries and assimilated into the local populations. Some of the Vandals (Silingi and Hasdingi) and Alans[164] also remained. The Suebians of northern and central Portugal and of Galicia were the most numerous of the Germanic tribes. Portugal and Galicia, (along with Catalonia which was part of the Frankish Kingdom), are the regions with the highest ratios today of Germanic Y-DNA in the Iberian peninsula.[citation needed]
Other minor – as well as later – influences include small Viking settlements between the 9th and 11th centuries, made by Norsemen who raided coastal areas mainly in the northern regions of Douro and Minho.[165][119][166][121]

The Moors occupied what is now Portugal from the 8th century until the Reconquista movement expelled them from the Algarve in 1249. Some of their population, mainly Berbers and Jews converted to Christianity and became New Christians (Cristãos novos); some descendants of these people are still identifiable by their new surnames.[167] Several genetic studies, including the most comprehensive genome-wide studies published on historical and modern populations of the Iberian Peninsula, conclude that the Moorish occupation left little to no Jewish, Arab and Berber genetic influence throughout most of Iberia, with higher incidence in the south and west, and lower incidence in the northeast; almost nonexistent in the Basque Country.[168][169][106][107]
Following the end of the Reconquista and the Conquest of Faro, religious and ethnic minorities such as the so-called "new Christians" or the "Ciganos" (Roma gypsies)[170] would later suffer persecution from the state and the Holy Inquisition. As a consequence, many were expelled and condemned under the Auto-da-fé[171] sentencing or fled the country, creating a Jewish diaspora in the Netherlands,[172] England, modern-day US,[173] Brazil,[174] The Balkans[175] as well as other parts of the world.
The emergence of the Portuguese Nation (868 AD onwards)
[edit]
The political origin of the Portuguese state is in the founding of County of Portugal in 868 (Portuguese: Condado Portucalense; in documents of the period the name used was Portugalia[176]). It was the first time in its history that a cohesive nationalism emerged, as even during the Roman Era, the indigenous populations were from diverse ethnic and cultural backgrounds.
Although the country was established as a county in 868, it was only after the Battle of São Mamede on 24 June 1128 that Portugal was officially recognised as a kingdom in virtue of the Treaty of Zamora and the papal bull Manifestis Probatum of Pope Alexander III. The establishment of the Portuguese state in the 12th century paved the way for the Portuguese to group together as a nation.[90][91][92]
A subsequent turning point in Portuguese nationalism was the Battle of Aljubarrota in 1385, linked to the figure of Brites de Almeida putting an end to any Castilian ambitions to take over the Portuguese throne.
Genetic comparisons
[edit]The Portuguese share a degree of ethnic characteristics with the Basques,[177] since ancient times. The results of the present HLA study in Portuguese populations show that they have features in common with Basques and some Spaniards from Madrid: a high frequency of the HLA-haplotypes A29-B44-DR7 (ancient Western Europeans) and A1-B8-DR3 are found as common characteristics. Many Portuguese and Basques do not show the Mediterranean A33-B14-DR1 haplotype, confirming a lower admixture with Mediterraneans.[138]
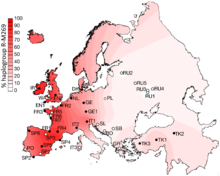
The Portuguese have a unique characteristic among world populations: a high frequency of HLA-A25-B18-DR15 and A26-B38-DR13, which may reflect a still detectable founder effect coming from ancient Portuguese, i.e., Oestriminis and Cynetes.[178] According to an early genetic study, the Portuguese are a relatively distinct population according to HLA data, as they have a high frequency of the HLA-A25-B18-DR15 and A26-B38-DR13 genes, the latter being a unique Portuguese marker. In Europe, the A25-B18-DR15 gene is only found in Portugal, and it is also observed in white North Americans and in Brazilians (very likely of Portuguese ancestry).[179]
The pan-European haplotype A1-B8-DR3 and the western-European haplotype A29-B44-DR7 are shared by Portuguese, Basques and Spaniards. The latter is also common in Irish, southern English, and western French populations.[179]
According to a genetic study of the human Y-chromosome haplogroup among the Portuguese conducted in 2005, men from mainland Portugal, the Azores and Madeira belonged to 78–83% of the "Western European" haplogroup R1b, and Mediterranean J and E3b.[180]
The comparative table shows statistics by haplogroups of Portuguese men with men of European countries, and communities.
| Country/Haplogroup | I1 | I2*/I2a | I2b | R1a | R1b | G | J2 | J*/J1 | E1b1b | T | Q | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portugal | 2 | 1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 56 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 3 | 14 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 0 |
| France | 8.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 3 | 58.5 | 5.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 |
| United Kingdom | 8 | 1 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 80 | 2 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Germany | 16 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 16 | 44.5 | 5 | 4.5 | 0 | 5.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Ireland | 6 | 1 | 5 | 2.5 | 81 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Italy | 4.5 | 3 | 2.5 | 4 | 39 | 9 | 15.5 | 3 | 13.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Spain | 1.5 | 4.5 | 1 | 2 | 69 | 3 | 8 | 1.5 | 7 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Ukraine | 4.5 | 20.5 | 0.5 | 44 | 8 | 3 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 |
| Ashkenazi Jews | 4 | 10 | 9 | 9.5 | 19 | 19 | 20.5 | 2 | 0.5 | 5 | 0 | 1.5 |
| Sephardi Jews | 1 | 5 | 13 | 15 | 25 | 22 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
Culturally and linguistically, the Portuguese are close to the Galicians who live in northwestern Spain.[181][182][183][184] The similarities among the two groups are very pronounced and some people claim that Galician and Portuguese are, in fact, the same language (see also: Reintegrationism).[185][186]
Demography
[edit]Demographics of Portugal
[edit]
There are around 9.15 million Portuguese-born people in Portugal,[187] out of a total population of 10.467 million[188] (87.4%).
Concerning citizenship, there are about 782,000 foreigners legally living in the country (7.47%), thus approximately 9.685 million people living in Portugal hold Portuguese citizenship or legal residency.[189]
Ageing is a major issue in Portugal as the median age stands at 46.8 years (while in the EU as a whole it is 44.4 years)[190] and people aged 65 or more now account for 23.4% of the total population.[191] This is due to a low total fertility rate (1.35 against the EU average of 1.53)[191] as well as to a very high life expectancy at birth (82.65).[192] Due to the high percentage of senior citizens, the crude mortality rate (12%)[193] exceeds the crude birth rate (7.6%).[194]
With respect to the infant mortality rate, Portugal boasts one of the lowest in the world (2.6%), attesting to a significant improvement in living conditions since 1961, when 8.9% of newborns would die.[195] The average age of women at first childbirth stands at 29.9 years, in contrast to the EU average of 28.2.[196]
About 66.85% of the population lives in urban settings, with the population being unevenly distributed and concentrated along the coast and in the Lisbon metropolitan area, where 2,883,645, or 27.67% of the population, live.[197][198]
About 64.88% of the national population, or 6,760,989 people, live in the 56 municipalities with more than 50,000 inhabitants, about 18.2% of all national municipalities. On the other hand, there are 122 municipalities, about 39.6% of all national municipalities, with a population of 10,000 inhabitants or less, totaling 678,855 inhabitants, about 6.51% of the national population.
Native minority languages in Portugal
[edit]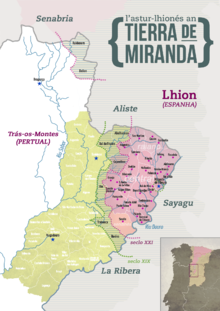
The main language spoken as first language by the overwhelming majority of the population is Portuguese.[199] Other autochthonous languages spoken include:
- Caló (see also Caló language), the language of the Portuguese-Romani community. There are about 52,000 Romani people in Portugal.[200]
- Mirandês (see also Mirandese language), officially recognised as an official language.[201] It enjoys special protection in the area of Miranda do Douro, Vimioso and Mogadouro. As of today, there are about 15,000 people who speak the language (0.14%).[202][203][204][205] The language is part of the Asturian-Leonese linguistic group which includes the Asturian and Leonese minority languages of Northwestern Spain.[206][207][208][209][210] All of the speakers are bilingual and speak Portuguese as well and code-switching is common.
- Barranquenhu (see also Barranquenho), spoken in the town of Barrancos (in the border between Extremadura and Andalusia, in Spain, and Portugal). As of today, there are about 3,000 speakers of the language (0.03%).[211] It is a dialect of Portuguese heavily influenced by Extremaduran and, more recently, southern Spanish.
- Minderico – a sociolect or argot spoken in Minde, practically extinct. There are about 150 speakers left[212][213]
- Portuguese Sign Language, the official language for the deaf community in Portugal. There are about 30,000 deaf people (0.29%) in Portugal who use the language.[214] The first teacher of deaf-mutes in France was Portuguese-Jew Jacob Rodrigues Pereira.
Ethnic minorities in Portugal
[edit]
People from the former colonies, particularly Brazil, Portuguese Africa (especially Afro-Portuguese), Macau, Portuguese India and Timor-Leste, have been migrating to Portugal since the 1900s.
A great number of Slavs, especially Ukrainians (now one of the biggest ethnic minorities[215][216]) and Russians, as well as Moldovans, Romanians, Bulgarians and Georgians, have been migrating to Portugal since the late 20th century. A new wave of Ukrainians arrived in Portugal after the Russian invasion of Ukraine, and there are now approximately 60,000 Ukrainian refugees in Portugal, making them the second largest migrant community in Portugal, after Brazil's. [217][218]
There is a Chinese minority of Macau Cantonese origin as well as of Chinese mainlanders.
Other Asian communities relevant in numbers include Indians, Nepalis, Bangladeshis and Pakistanis while, dealing with Latin Americans, Venezuelans – numbering about 27,700 – are particularly present.[219]
In addition, there is a small minority of Romani – about 52,000 in number.[220][221]
Portugal is also home to other EU and EEA/EFTA nationals (French, Germans, Dutch, Swedes, Spaniards). The UK and France represented the largest senior residents communities in the country as of 2019, they are part of a larger expatriate community including Germans, Dutch, Belgians and Swedes as well.[222]
Officially registered foreigners accounted to 7.3% of the population,[189] with the tendency to increase further.[223] These include both citizens born in Portugal with foreign citizenship and foreign immigrants. Descendants of immigrants are excluded (Portugal, like many European countries, does not collect data on ethnicity) and those who, regardless of place of birth or citizenship at birth, were Portuguese citizens (see also Portuguese nationality law).
Dealing with religious minorities, there are also about 100,000 Muslims[224][225] and an even smaller minority of Jews of about 5,000–6,000 people (the majority are Sephardi such as the Belmonte Jews, while some others are Ashkenazi).[226][227][228][229]
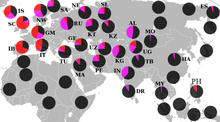
- Flag maps of the five most important foreign communities[a] in each Portuguese district as of 01.01.22[230]
-
Flag map of the most common foreign nationality in Portugal per each district. One can see the importance of the Brazilian immigration as well as the influx of Venezuelans in Madeira, Britons in Algarve and Indians in Beja
-
Flag map of the second most common foreign nationality in Portugal in every district. Cape Verdeans are present in Lisbon Area, Italians in Porto while Britons and Romanians in the interior.
-
Flag map of the third most common foreign nationality in Portugal in every district. US-citizens are present in the Azores, Chinese in the industrialized north while PALOP citizens in the Lisbon metropolitan area
-
Flag map of the fourth most common foreign nationality in Portugal in every district. Angolans and Eastern Europeans (such as Ukrainians in Santarém) are present nationwide
-
Flag map of the fifth most common foreign nationality in Portugal in every district. One can appreciate the presence of the Chinese near the Spanish border and the prevalence of Europeans along the coast
Portuguese surnames
[edit]
A Portuguese surname is typically composed of a variable number of family names (rarely one, often two or three, sometimes more). The first additional names are usually the mother's family surname(s) and the father's family surname(s). For practicality, usually only the last surname (excluding prepositions) is used in formal greetings.
Portugal has a highly adaptable naming system that complies with the country's legal framework. The law mandates that a child must be given at least one personal name and one surname from either parent. Additionally, there is a limit to the number of names that can be given, which is set at a maximum of two personal names and four surnames.[231]
In pre-Roman times, the inhabitants of what is now Portugal had either a single name or a name followed by a patronym, which reflected their ethnicity or the tribe/region they belonged to. These names could be Celtic, Lusitanian, Iberian, or Conii. However, the Roman onomastic system began to slowly gain popularity after the first century AD. This system involved adopting a Roman name or the tria nomina, which consisted of a praenomen (given name), nomen (gentile), and cognomen. Today, most Portuguese surnames have a Germanic patronymic (such as Henriques, Pires, Rodrigues, Lopes, Nunes, Mendes, Fernandes etc. where the ending -es means "son of"), locative (Gouveia, Guimarães, Lima, Maia, Mascarenhas, Serpa, Montes, Fonseca, Barroso), religious origin (Cruz, Reis, De Jesus, Moysés, Nascimento), occupational (Carpinteiro (carpenter), Malheiro (wool-maker, thresher), Jardineiro (gardener), or derived from physical appearance (Branco (white), Trigueiro (brown, tanned), Louraço (blond). Toponymic, locative, and religion-derived surnames are often preceded by the preposition 'of' in its varying forms: (De, de), (Do, do- masculine), (Da, da- feminine) or 'of the' (dos, Dos, das, Das – plural) such as De Carvalho, Da Silva, de Gouveia, Da Costa, da Maia, do Nascimento, dos Santos, das Mercês. If the preposition is followed by a vowel, sometimes apostrophes are used in surnames (or stage names) such as D'Oliveira, d'Abranches, d'Eça. In some previous Portuguese colonies in Asia (India, Malaysia, East Timor) there are alternative spellings such as 'D'Souza, Desouza, De Cunha, Ferrao, Dessais, Balsemao, Conceicao, Gurjao, Mathias, Thomaz.
Below there is a list of the most frequent 25 surnames in Portugal; the "percent frequency" figures are higher than one might expect because the majority of Portuguese individuals have multiple surnames. To illustrate, if we assume that surname distribution is relatively uniform (at least for those with high frequency), we can infer that roughly 0.5626% (9.44 x 0.0596) of the Portuguese population carries both the surnames Silva and Santos simultaneously.[232][233][234]
| Rank | Surname | Percent Frequency | Absolute Frequency (in 1,000s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Silva | 9.44% | 999 |
| 2 | Santos | 5.96% | 628 |
| 3 | Ferreira | 5.25% | 553 |
| 4 | Pereira | 4.88% | 514 |
| 5 | Oliveira | 3.71% | 391 |
| 6 | Costa | 3.68% | 387 |
| 7 | Rodrigues | 3.57% | 376 |
| 8 | Martins | 3.23% | 340 |
| 9 | Jesus | 2.99% | 315 |
| 10 | Sousa | 2.95% | 311 |
| 11 | Fernandes | 2.82% | 297 |
| 12 | Gonçalves | 2.76% | 291 |
| 13 | Gomes | 2.57% | 271 |
| 14 | Lopes | 2.52% | 265 |
| 15 | Marques | 2.51% | 265 |
| 16 | Alves | 2.37% | 250 |
| 17 | Almeida | 2.27% | 239 |
| 18 | Ribeiro | 2.27% | 239 |
| 19 | Pinto | 2.09% | 220 |
| 20 | Carvalho | 1.97% | 208 |
| 21 | Teixeira | 1.69% | 178 |
| 22 | Moreira | 1.54% | 162 |
| 23 | Correia | 1.53% | 161 |
| 24 | Mendes | 1.39% | 146 |
| 25 | Nunes | 1.32% | 139 |
Portuguese diaspora
[edit]Overview
[edit]Portugal has traditionally been a land of emigration: according to estimates, in the whole world there could easily be more than one hundred million people with recognizable Portuguese ancestors, with Portuguese diasporas found everywhere, in many diverse regions around the globe in all continents. Due to the extent of the phenomenon and lack of sources dealing with statistics dating hundreds of years ago, the total number of people of Portuguese descent is hard to estimate.[235][236][237]
The extension of the phenomenon is due to explorations carried in the 15th and 16th centuries as well as to the subsequent colonial expansion. Colonization encouraged worldwide emigration of Portuguese from the 15th century onwards to South Asia, the Americas, Macau, East-Timor, Malaysia, Indonesia, Myanmar[238] and Africa, particularly to the former colonies (see Luso-Africans). Portuguese emigration also contributed to the settlement of the Atlantic islands, the population of Brazil (where the majority of the current population is of Portuguese descent) and the formation of communities of partial-Portuguese ethnic-cultural origin – as in Goa Catholic Goans, in Sri Lanka Portuguese Burghers, in Malacca the Kristang and in Macau the Macaense. The Portuguese Empire, which lasted nearly 600 years, ended when Macau was returned to China in 1999. As a consequence, during those 600 years, millions of people left Portugal. As a result of inter-ethnic marriage and cultural influences, dialects based on Portuguese have occurred both in the former colonies (e.g. Forro) and in other countries (e.g. Papiamentu).
In addition, a considerable segment of the Portuguese communities abroad is due to recent mass emigration phenomena, mainly driven by economic reasons, dating to the 19th and 20th centuries. In fact, between 1886 and 1966 Portugal, after Ireland, was the second Western European country to lose more people to emigration.[239]
From the middle of the 19th century to the late 1950s, nearly two million Portuguese left Europe to live mainly in Brazil and with significant numbers to the United States, Canada and the Caribbean.[240] About 1.2 million Brazilian citizens are native Portuguese.[241] Significant verified Portuguese minorities exist in several countries (see table below).[242]
By 1989 some 4,000,000 Portuguese citizens were living abroad, mainly in France, Germany, Brazil, South Africa, Canada, Venezuela, and the United States.[243] Estimates from 2021 point that as much as 5 million Portuguese citizens (thus not taking into account descendants or citizens not registered within the Portuguese consular authorities) may be living abroad.[244]
Within Europe, substantial concentrations of Portuguese may be found in Francophone countries like France, Luxembourg and Switzerland, spurred in part by the linguistic proximity that exists between the Portuguese and the French language. In fact, according to data from the General Directorate of Consular Affairs and Portuguese Communities of the Portuguese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the countries with the largest Portuguese communities are, in ascending order of demographic importance, France, the UK and Switzerland.[245]
Generally speaking, Portuguese diaspora communities often feel a strong bond to the land of their ancestors, their language, their culture and their national dishes such as cod.
Portuguese Sephardi Jews
[edit]
Dating back many centuries, descendants of Portuguese Sephardi Jews are found everywhere in the world, with notable communities having settled in significant numbers in Israel, the Netherlands, the United States, France, Venezuela, Brazil and Turkey.
The Expulsion
[edit]The Portuguese Jewish diaspora was mainly a result of the expulsion decree[246] issued in 1496 by the Portuguese monarchy, which targeted Jews living in Portugal. This decree forced many Jews to either convert to Christianity (leading to the emergence of Cristão-novos and of Crypto-Judaism practices) or to leave the country, leading to a diaspora of Portuguese Jews throughout Europe and Brazil. In Brazil[247] many of the early colonists were also originally Sephardi Jews who, following their conversion, were known as New Christians (see Anusim).[248][249]
The Emigration

It is believed that up to 10,000 Portuguese-Jews might have migrated to France from 1497; this phenomenon remained noticeable up until the 1600s, when the Netherlands became a favourite choice.[250][251]
The Netherlands and England became in fact top destinations for Portuguese-Jewish emigrants due to the absence of the Inquisition. Other that adding to the economical and cultural aspects of their host countries,[252] the Portuguese-Jews also established institutions that are still present, such as the Esnoga, in Amsterdam, The Congregation Shearith Israel – the oldest Jewish congregation in the United States – , Bevis Marks Synagogue – the oldest synagogue in the United Kingdom – the Spanish and Portuguese Synagogue of Montreal – the oldest synagogue in Canada – , Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, City Lights Booksellers & Publishers or the David Cardozo Academy in Jerusalem.
Minor communities thrived in the Balkans,[253] Italy,[254] the Ottoman Empire[255][256] and Germany, especially in Hamburg (see Elijah Aboab Cardoso Joan d'Acosta and Samuel ben Abraham Aboab).[257]
Portuguese-Jews were also responsible for the appearance of Papiamentu[258] (a 300,000 speakers-strong[259] Portuguese-based creole now official language in Aruba, Curaçao and Bonaire) and of Sranan Tongo, an English-based creole influenced by Portuguese spoken by more than 500,000 people in Suriname.[260][261]
The Shoah
During the Shoah, nearly 4,000 Jews of Portuguese descent residing in the Netherlands lost their lives, making up the largest group of casualties with a Portuguese background in the Nazi German genocide.[262][263] Among famous Portuguese-Jewish victims of the Shoah is painter Baruch Lopes Leão de Laguna. It is worth highlighting that, although officially neutral, the Portuguese regime at that time, Estado Novo, aligned with Germany's ideology and failed to fully protect its citizens and other Jewish people living overseas.[264][265][266] Despite the lack of support by the Portuguese authorities, some Jews of both Portuguese[267] and non-Portuguese descent, were saved thanks to the actions of individual citizens such as Carlos Sampaio Garrido, Joaquim Carreira, José Brito Mendes and the well known case of Aristides de Sousa Mendes,[268] who alone helped 34,000 Jews escaping Nazi violence.[269]
Portuguese-Jews nowadays
Over 500 years after the expulsion decree, in 2015 the Portuguese parliament officially acknowledged the expulsion of its citizens of Jewish descent as unrightful. To try and make up for long-lasting historical injustices, the government passed a law known as "Law of Return".[270] The law aimed to right the historic wrongs of the Portuguese Inquisition, which resulted in the expulsion or forced conversion of thousands of Jews from Portugal in the 15th and 16th centuries. The law grants citizenship to any descendants of those persecuted Jews able to confirm their Sephardic Jewish ancestry and a "connection" to Portugal. It is intended to provide a measure of justice and recognition to those whose families suffered from discrimination and persecution five centuries prior.[271][272][273][274]
Since 2015, more than 140,000 people of Sephardic descent, from 60 countries (mostly from Israel or Turkey) applied for Portuguese citizenship.[275][276][277][278] Unfortunately, soon after this law was approved, it transpired that a number of foreigners with no legitimate historical Sephardic links were granted Portuguese citizenship, among those, Russian oligarch Roman Abramovich became Portuguese – thus EU – citizens under the new law. Due to cases of abuse and loopholes in this law which was meant as reparation towards a minority, the judiciary was prompted to intervene and review this law.[279][280][281][282]
Notable people of Portuguese-Jewish descent include:
- Amatus Lusitanus (1511–1568): Jewish physician said to have discovered the valves in the azygos vein.
- Gracia Mendes Nasi (1510–1569): Philanthropist and one of the wealthiest Jewish women of Renaissance Europe
- Leonora Duarte (1610–1678): a Flemish composer and musician
- Baruch Spinoza (1632–1677): Dutch philosopher of Portuguese-Jewish origin
- Catherine da Costa (1679–1756): English miniaturist
- David Ricardo (1772–1823): a British political economist
- Rehuel Lobatto (1797–1866): Dutch mathematician whose notable contributions include Gauss-Lobatto quadrature method and the Lobatto polynomials
- Isaäc da Costa (1798–1860): a Jewish poet.
- Pereire brothers (19th century): major figures in the development of France's finance and infrastructure
- Samuel Sarphati (1813–1866): Dutch physician and Amsterdam city planner
- Solomon Nunes Carvalho (1815–1897): American painter, photographer, author and inventor
- Grace Aguilar (1816–1847): English novelist, poet and writer on Jewish history and religion
- Camille Pissarro (1830–1903): a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter considered the "dean of the Impressionist painters"[283]
- Francis Lewis Cardozo (1836–1903): American clergyman, politician, and educator. When elected in South Carolina as Secretary of State in 1868, he was the first African American to hold a statewide office in the United States
- Maud Nathan (1862–1946): American social worker, labor activist and women's suffragist
- Federigo Enriques (1871–1946): Italian mathematician, now known principally as the first to give a classification of algebraic surfaces in birational geometry, and other contributions in algebraic geometry
- Frieda Belinfante (1904–1995): Dutch cellist, philharmonic conductor, a prominent lesbian, and a member of the Dutch resistance during World War II
- William Leonard Pereira (1909–1985): American architect
- Abraham Pais (1918–2000): Dutch-American physicist and science historian
- Louisa Benson Craig (1941–2010): Burmese-born two-time beauty pageant winner and Karen rebel leader of Portuguese-Jewish descent[284][285]
- Alberto Portugheis (1941): Argentine pianist
- Henrique Cymerman (1959): Israeli journalist
- Shon Weissman (1996): Israeli footballer
The Americas outside of Brazil
[edit]The United States

The United States has had bilateral relations with Portugal since its early years. After the American Revolutionary War, Portugal became the first neutral country to acknowledge the United States.[286]
Despite Portugal never colonizing—nor attempting to colonize—the current territory of the United States of America, navigators such as João Fernandes Lavrador, Miguel Corte-Real and João Rodrigues Cabrilho are among the earliest documented European explorers. The Dighton Rock, in Southeastern Massachusetts, is a testimony of the early Portuguese presence in the country.[287][288][289][290]
Mathias de Sousa, who was potentially a Sephardic Jew of mixed African background, is believed to be the first documented Portuguese resident of colonial United States.[291] Additionally, one of the earliest Portuguese Jews in the United States, Isaac Touro, is commemorated in the name of the country's oldest synagogue, the Touro Synagogue.
Despite the relations between the two countries dating hundreds of years, the Portuguese started to settle in significant numbers only in the 19th century, with major migration waves occurring in the first half of the 20th century, especially from the Azores.[292][293][294][295] Of the 1,4 million Portuguese Americans found in the nation today (0.4% of the US population) the majority of them are originally from the Azores. Not only the arrival of Azorean emigrants was easier because of geographic proximity, but it was also encouraged by the Azorean Refugee Act of 1958, sponsored by Massachusetts senator John F. Kennedy and Rhode Island senator John Pastore so as to help the population affected by the 1957–58, the Capelinhos volcano eruption.[296][297][298] Moreover, it is noteworthy that the 1965 Immigration Act stated that if someone had legal or American relatives in the United States who could serve as a sponsor, they could be given the status of legal aliens. This act dramatically increased Portuguese immigration into the 1970s and 1980s.[299]
Major Portuguese communities are found in New Jersey (particularly in Newark), the New England states, California and along the Gulf Coast (Louisiana). Springfield, Illinois once possessed the largest Portuguese community in the Midwest.[300] In the Pacific, Hawaii (see Portuguese immigration to Hawaii) has a sizable Portuguese population, encouraged by the availability of labor contracts on the islands 150 years ago.[301]
The Portuguese community in the US is the second largest in the Americas after the one found in Brazil.
Canada
Canada, particularly Ontario, Quebec and British Columbia, has developed a significant Portuguese community since the 1940s. The availability of more job opportunities in Canada attracted a significant number of Portuguese migrants, leading to the flourishing of Portuguese culture in the subsequent decade. Many Portuguese residents took the initiative to purchase homes and establish their own businesses, resulting in contributing to the Canadian cultural landscape.
According to the 2016 Census, there were 482,610, or 1.4% of Canadians, who claimed full or partial Portuguese ancestry.[302]
Two major neighbourhoods where the Portuguese heritage is particularly present include Little Portugal, in both Toronto and Montréal. Montréal's Little Portugal, known as "Petit Portugal" in French, is adorned with numerous Portuguese shops, restaurants, and cafes, and it is also home to "Parc du Portugal" (Portugal's park), embellished with vibrant murals and elements inspired by Portuguese design.[303][304]
Portuguese Canadians are proud of their heritage and, despite the geographical distance between the two countries, interest towards the language remains vivid.[305][306][307] Recent statistics reveal that the Portuguese language is spoken by over 330,000 Canadians, making up around 1% of the population.[308] It is considered one of the most significant cultural contributions that the Portuguese have made to Canada, adding to its diversity and enriching the country as a whole.[309][310][311]
Despite the growth the community has seen in the 20th century, significant testimonies of the Portuguese presence in Canada include the name of one of the 10 provinces of Canada: Newfoundland and Labrador. King Henry VII coined the name "New found land" for the territory explored by Sebastian and John Cabot.. In Portuguese, the land is known as Terra Nova, which translates to "new land," and is also referred to as Terre-Neuve in French, the name for the province's island region. The name Terra Nova is commonly used on the island, including in the name of Terra Nova National Park. The influence of early Portuguese exploration is evident in the name of Labrador, which is derived from the surname of Portuguese navigator João Fernandes Lavrador.[312] Other remnants of early Portuguese exploration include toponyms such as Baccalieu (from bacalhau, Portuguese for codfish) and Portugal Cove. Portuguese cartographer Diogo Ribeiro is responsible for one of the earliest maps depicting the territory of modern-day Canada.[313]
The Caribbean
There are Portuguese influenced people with their own Portuguese-influenced culture and Portuguese-based dialects in parts of the world other than former Portuguese colonies. In the Caribbean, in particular, although never colonized by the Portuguese, the Lusitanian heritage remains strong thanks to the migrants that from the 1830s came as indentured labourers, especially from Madeira. In fact, although the first Portuguese who settled in the region were merchants or Portuguese-Jews fleeing the Portuguese Inquisition,[314] the mass migration that took place in the 19th century coincided with the abolition of slavery in the British colonies. As a result, the Portuguese, along with Indians and Chinese, were called upon to replace slave labor. The Portuguese took a prominent part in shaping the population of the West Indies and today their descendants form an active minority in many countries across the region.
As part of a larger system of low-wage labour, about 2,500 Portuguese left for Antigua and Barbuda[315] (where, as of today, little more than 1,000 people still speak the language),[316] 30,000 to Guyana (4.3% of the population in 1891)[317] (see Portuguese immigrants in Guyana) and another 2,000 settled in Trinidad and Tobago (see Portuguese immigrants in Trinidad and Tobago)[318][319][320] between the mid-1800s and the mid-1900s.[321][322][323] With regards to Guyana the Portuguese heritage is still alive in the numerous enterprises established by members of the community. Despite today numbering about 2,000 people, the Portuguese community's contributions are recognized and recently (2016) the second international airport of the country was renamed after a Portuguese Guyanese individual.[321][324]
Portuguese fishermen, farmers and indentured labourers dispersed also across other Caribbean countries, especially in Jamaica (about 5,700 people, primarily of Portuguese-Jewish descent),[325][326][327][328][329] St. Vincent and the Grenadines (0.7% of the population),[330] the briefly reclaimed by the Portuguese Empire island of Barbados – where there is still high influence from the Portuguese community[331] and Suriname (see Portuguese immigrants in Suriname). Dealing with Suriname, it is noteworthy that its first capital, Torarica (literally "rich Torah" in Portuguese), was established by Portuguese-Jewish settlers. Minor communities exist in Grenada,[332] Saint Lucia,[333] Saint Kitts and Nevis[334] and the Cayman Islands[335]
In the Caribbean territories of Overseas France there are about 4,000 Portuguese people, especially in Saint Barthélemy (where they constitute about a third of the population), Guadeloupe and Martinique.[336][337][338]
Portuguese heritage is still very tangible in Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao. In the three territories, the official language, Papiamentu, retains numerous Portuguese elements.
Moreover, the North Atlantic archipelago of Bermuda (10%[339] to 25%[340] of the population) has had sustained immigration especially from the Azores, as well as from Madeira and the Cape Verde Islands since the 1840s.[341]
Latin America (excluding Brazil)

Mexico (see Portuguese Mexicans) has had flows of Portuguese immigration since the colonial period until the early 20th century, the most important settlements are in north eastern cities,[342] such as Saltillo, Monterrey, Durango and Torreon. Santiago Tequixquiac, due to its natural conditions and its lime and stone mining deposits, was a place of settlement for Portuguese Crypto-Jews during the colonial period, they were brought there together with the Tlaxcalans and peninsular Spaniards to appease the Otomi indigenous people, in that town. Many Lusitanian cultural traits were preserved throughout the 19th century, such as forcados, gastronomy, some Sephardic customs and the surnames of its inhabitants. Every year dozens of young people seek to experience the adventure of catching a bull in the bullring, and one of the Portuguese traditions that prevail in Mexico.[343] A notable Portuguese-Mexican Jew was Francisca Nuñez de Carabajal, executed by burning at the stake by the Inquisition for judaizing in 1596.
Portuguese communities are also present in Central American countries such as Cuba, Dominican Republic or Puerto Rico.[344] Notable members of the community include activist Ada Bello, businesswoman Alexis Victoria Yeb, former Nicaraguan First Lady Lila Teresita Abaunza and Felipa Colón de Toledo.
Venezuela has the biggest number of Portuguese people in Latin America after Brazil (see Portuguese Venezuelans) . Portuguese started arriving to Venezuela in the early and middle 20th century as economic immigrants particularly from Madeira.[345] In Venezuela about 1.3 million people (4.61% of the population) is of Portuguese descent.[345] The emigration towards Venezuela occurred mainly in the 1940s and 1950s. The extense Luso-Venezuelan community includes personalities such as María Gabriela de Faría, Marjorie de Sousa, Vanessa Gonçalves, Kimberly Dos Ramos and Laura Gonçalves.
Colombia did not witness mass Portuguese immigration, since the Portuguese tended to move to countries where immigration was not curbed but promoted, such as Brazil and Venezuela. Although Portuguese may have explored the area during the Age of Discovery, there is not evidence that they established communities in nowadays Colombia. It is noteworthy that Colombia was under full Spanish sovereignty, as defined by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The Portuguese embassy in Bogota estimates that there are around 800 Portuguese nationals who live in Colombia, although the numbers could be much higher as Portuguese are not obliged to register their presence within consulates abroad. The number of people of Portuguese ancestry is not known, but it is safe to assume that they have integrated very well in the Colombian society and are indistinguishable, except for some surnames, from other Colombians.[346][347]
In Peru, Portuguese immigration gradually began at the time of the Viceroyalty of Peru until the beginning of the 19th century, without being massive. Many sailors who traveled along the Peruvian coast, and later entered the country following the route from the Atlantic through the Amazon River established themselves in Peru, intermarrying with local people. There are also records of Luso-Brazilians in the cities surrounding the Brazil-Peru border. Although the number of Portuguese citizens in Peru is not high (about 2,000 people),[348] Peruvians with Portuguese ancestors could easily be as much as 1 million people, including direct and indirect descendants, which represents about 3% of the national total.[349] A famous Peruvian of Portuguese descent is popular TV presenter Janet Barboza.

The Cono Sur region had Portuguese immigration since the early 20th century. The community in Argentina (See Portuguese Argentines and Cape Verdean Argentines), Uruguay (see Portuguese Uruguayans) and Chile numbers around 255,000 people combined[350][351][352] (0.37% of the population of the region).
In particular, Portuguese Uruguayans are mainly of Azorean descent[353] even though Portuguese presence in the country dates back to the colonial times, in particular to the establishment of Colonia del Sacramento by the Portuguese in 1680,[354] which eventually turned into a regional center of smuggling. Other Portuguese entered Uruguay as Brazilians of Portuguese descent, who crossed the border into the country ever since it became independent from Brazil itself. During the second half of the 19th century and part of the 20th, several additional Portuguese immigrants arrived; the last wave was during 1930–1965.[355][356] As of 2021, 3,069[357] Portuguese citizens have registered as residing in Uruguay within Portuguese authorities. In addition to Portuguese citizens, there are also many luso-descendants (lusodescendentes) whose numbers are hard to estimate.[358][350]

Argentina-Portugal relations date back to the early European explorations in the region, as the Río de la Plata (literally, silver river) was first explored by the Portuguese in the 1510s. In Argentina, Portuguese immigration has been relatively limited due to a preference for the Portuguese-speaking neighboring Brazil. However, the Portuguese constituted the second-largest immigrant group after the Spanish before 1816 and continued to arrive throughout the 19th century. While a significant number settled in the interior of the country, with the primary destination for Portuguese immigrants being Buenos Aires. Many men from Lisbon, Porto, and coastal regions of Portugal, with diverse occupations but predominantly in maritime professions such as sailors, stevedores, and porters, were already present in these areas. During the 1970s, they began to organize themselves ethnically, and over the following decades, community life, including mutual support organizations, clubs, and newspapers, became more active.[359][360] A popular member of the Portuguese community in Argentina was best-selling author Silvina Bullrich.
Africa
[edit]
In the early twentieth century the Portuguese government encouraged white emigration to Angola and Mozambique, and by the 1970s, there were up to 1 million Portuguese settlers living in their overseas African provinces.[361] Minor communities also settled in Guinea-Bissau, Equatorial Guinea, Cape Verde and São Tomé and Príncipe, Portuguese influences are still found in these countries, where Portuguese enjoys the status of official language.
Following the Carnation Revolution, as the country's African possessions gained independence in 1975, An estimated 800,000 Portuguese returned to Portugal or moved to other countries. For many, Portugal was more an historical homeland than the actual country of birth. Despite this, thousands of people left and went to a country they had never been to.[362] These people are often referred as Retornados (literally, those who came back).
Other Portuguese moved to South Africa, Brazil, Botswana and Algeria.[363][364][365][366][367] In particular, in South Africa there is now the largest Portuguese community in the continent, numbering about 700,000 people (more than the city of Lisbon itself).
Portuguese descendants still make up a significant minority in the former colonies where, as a result of intermarriage and cultural influences, they form the bulk of Mestiços (Mixed African-European people).[368][369][370][371]
In Europe outside of Portugal
[edit]France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Monaco, Andorra and Switzerland







Due to the linguistic proximity between Portuguese and French and the plurality of schools in Portugal which promotes French as foreign language many Portuguese nationals started migrating towards French speaking countries in Europe (namely, France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Monaco and the French-speaking part of Switzerland) in the 1960s, for economic reasons and to avoid conscription to fight in Portuguese Overseas provinces. Interestingly, migration to Andorra - where, although Catalan is the sole official language, French is widely spoken - made the Portuguese the third largest ethnic group in the state, after Andorrans and Spaniards.[372][373][374][375]
According to the most recent estimates of both Eurostat and INE, around 15.4% of Portuguese people are fluent in French.[376][377] Although relatively popular still, French has been dwindling, and English is taught in schools as a global language. For instance, in 2005 the proportion of Portuguese adults fluent in French stood at 24%[378] which indicates a clear decline in younger speakers. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy noticing that 70% of middle school students study French.[379] French media are widely available in Portugal (newspapers, magazines, radio stations and TV channels) and many libraries still offer a French-language section.
Some Portuguese migration to the more affluent French speaking countries in Europe exists, although not as significant as in post-WWII decades.
Between France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Monaco, Andorra and Switzerland there are more than 2,260,000 Portuguese citizens and, taking int account People with Portuguese ancestry not holding Portuguese nationality their numbers could easily soar up to 2,7 million: for instance, France alone hosts 450,000 Luso-descendants or lusodescendentes. In fact, with more than 1,55 million Portuguese citizens[380] and up to 2 million people of Portuguese descent,[381] France hosts, by far, the largest community of Portuguese people outside of Portugal, second only to Brazil (see Portuguese in France).
There are records of Portuguese people living in France since the early centuries of the Portuguese kingdom, notably merchants but also Portuguese-Jews and Portuguese nobles: even Louis XIV or "le Roi Soleil" was of Portuguese descent through his grandfather Philip II. Despite their being present in the country for centuries, Portuguese nationals have only relatively recently started to move to France in large numbers: for comparison, there were less than 40,000 Portuguese in France on the eve of WWII.[382][383]
From the 1960s, the economic stagnation of Brazil, a traditional destination, measures taken by France to attract Portuguese workers, António de Oliveira Salazar's dictatorship and the colonial wars, were all factors that contributed to 1,000,000 people fleeing Portugal and going to France from 1960 to 1974.[384][385][386][387][388] After 1974, despite remaining a major destination for Portuguese migrants, Portuguese nationals have started moving to Luxembourg and Monaco (1980s), Switzerland (1990s) and – increasingly – Belgium and Andorra (2000s). This is also due to the tightening control of immigration by French authorities following the 1973 oil crisis.[389][390][391][392]
Portuguese constitute 23.4% of the population of Luxembourg, which makes them one of the largest ethnic groups as a proportion of the total national population, second only to native Luxembourgers (see Portuguese in Luxembourg). Andorra is inhabited by 16,300 Portuguese nationals (19.4% of the population)[393][394], Monaco hosts around 1,000 Portuguese nationals (3.3% of the Population)[395] while Belgium is home to around 80,000 Portuguese nationals (0.7% of the population).[396]
In Switzerland, Portuguese have settled mainly in Romandy. In fact, while official figures suggest that Portuguese is spoken by 5% of the population of Switzerland as a whole at home - by comparison Italian, an official language of Switzerland, is spoken by 8.8% - the figure rises to 10.1% in French speaking Switzerland, thus making Portuguese the most spoken language in the region's households, second only to French. Around 460,000 Portuguese nationals live in the country according to the latest estimates (5.3% of Switzerland's population).[397]
Famous Swiss people of Portuguese descent include snooker player Alexander Ursenbacher, models Pedro Mendes and Nomi Fernandes, actress Yaël Boon and Olympic medalist Stéphane Lambiel.
Notable Belgians of Portuguese descent include – apart from nobles such as Queen Elizabeth or King Leopold III – fashion designer Veronique Branquinho, footballer Yannick Carrasco, actress Rose Bertram, sprinter Jonathan Sacoor and actress Helena Noguerra.
Despite Portuguese migration towards these countries has steadily declined over the years, from 2003 to 2022 around 615,000 Portuguese nationals have moved towards these countries, especially during the years following the 2008 financial crisis. Interestingly, as of 2021 around 40% has returned to Portugal, in particular after 2015, when the economic outlook the Mediterranean country bettered significantly.[398]
| 2003–2006 | 2007–2010 | 2011–2014 | 2015–2018 | 2019–2022 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switzerland | 50,346 | 59,329 | 69,172 | 40,438 | 33,608 | 252,893 |
| France | 39,960 | 33,708 | 68,216 | 40,345 | 28,967 | 211,196 |
| Luxembourg | 14,956 | 16,605 | 18,592 | 16,723 | 14,556 | 81,432 |
| Belgium | 7,694 | 11,064 | 14,693 | 11,297 | 9,029 | 53,777 |
| Andorra | 7,167 | 3,204 | 1,067 | 1,122 | 884 | 13,444 |
| Total | 120,123 | 123,910 | 171,740 | 109,925 | 87,044 | 612,742 |
Germany
In the post-war period, Hundreds of thousands of Portuguese settled as guest workers in other European countries, especially in Western Europe. On 17 March 1964, the recruitment agreement between the Federal Republic of Germany and Portugal was signed under the Erhard I cabinet. The Portuguese Armando Rodrigues de Sá was officially welcomed in 1964 as the millionth "guest worker" in Germany and was given a certificate of honor and a two-seater Zündapp Sport Combinette – Mokick.[400] The number of Portuguese citizens living in Germany is estimated at 245,000 as of 2021.[401] The largest Portuguese community is located in Hamburg with about 25,000 people with Portuguese descent. There is also a Portugiesenviertel (Portuguese quarter) in Hamburg near the Port of Hamburg and between the subway stations of Landungsbrücken and Baumwall where many Portuguese restaurants and cafes are located there.
The United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, people of Portuguese origin were estimated at 400,000 in 2021 by Portuguese authorities (see Portuguese in the United Kingdom).[402][403] Although unconfirmed, other sources claim that there might be as much as 500,000 Portuguese in the country,[404] a considerably higher than the estimated 170,000 Portuguese-born people residing in the country in 2021[405] (this figure does not include British-born people of Portuguese descent).
In areas such as Thetford and the crown dependencies of Jersey and Guernsey, the Portuguese form the largest ethnic minority groups at 30% of the population, 9.03% and 3.13% respectively.
The British capital London is home to the largest number of Portuguese people in the UK, with the majority being found in the Western boroughs of Kensington and Chelsea, Lambeth and Westminster.[406]
Portuguese ancestry in the Brazilian population
[edit]| Source: Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics (IBGE) | |||||||||||||
| Decade | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationality | 1500–1700 | 1701–1760 | 1808–1817 | 1827–1829 | 1837–1841 | 1856–1857 | 1881–1900 | 1901–1930 | 1931–1950 | 1951–1960 | 1961–1967 | 1981–1991 | 1991–2023 |
| Portuguese | 100,000 | 600,000 | 24,000 | 2,004 | 629 | 16,108 | 316,204 | 754,147 | 148,699 | 235,635 | 54,767 | 4,605 | 400,000 |

Due to the emigration of a significant part of the Portuguese towards Brazil, they played a particularly important role in the formation of Brazilians as a nation, becoming one of its main components. In fact, given the shared past and the fact that Portuguese deeply influenced the formation of Brazilians as a nation, the Portuguese are the largest European immigrant group in Brazil. In colonial times, over 700,000 Portuguese settled in Brazil, and most of them went there during the gold rush of the 18th century.[407] Brazil received more European settlers during its colonial era than any other country in the Americas. Between 1500 and 1760, about 700,000 Europeans immigrated to Brazil, compared to 530,000 European immigrants in the United States.[408][409] They managed to be the only significant European population to populate the country during colonization, even though there were French and Dutch invasions. The Portuguese migration was strongly marked by the predominance of men (colonial reports from the 16th and 17th centuries almost always report the absence or rarity of Portuguese women). This lack of women worried the Jesuits, who asked the Portuguese King to send any kind of Portuguese women to Brazil, even the socially undesirable (e.g. prostitutes or women with mental maladies such as Down Syndrome) if necessary.[410][411] The Crown responded by sending groups of Iberian orphan maidens to marry both cohorts of marriageable men, the nobles and the peasants. Some of which were even primarily studying to be nuns.[410][412]
The Crown also shipped over many Órfãs do Rei of what was considered "good birth" to colonial Brazil to marry Portuguese settlers of high rank. Órfãs do Rei literally translates to "Orphans of the King", and they were Portuguese female orphans in nubile age. There were noble and non-noble maidens and they were daughters of military compatriots who died in battle for the king or noblemen who died overseas and whose upbringing was paid by the Crown. Bahia's port in the East received one of the first groups of orphans in 1551.[413] In colonial Brazil, the Portuguese men competed for women, because among the African slaves and the female component of Indigenous peoples of the Americas were minorities.[414] This explains why the Portuguese men left more descendants in Brazil than the Amerindian or African men did. The Indigenous and African women were "dominated" by the Portuguese men, preventing men of color to find partners with whom they could have children. Added to this, White people had a much better quality of life and therefore a lower mortality rate than the black and indigenous population. Then, even though the Portuguese migration during colonial Brazil was smaller (3.2 million Indians estimated at the beginning of colonization and 4.8 million Africans brought since then, compared to the descendants of the over 700,000 Portuguese immigrants) the "white" population (whose ancestry was predominantly Portuguese) was as large as the "non-white" population in the early 19th century, just before independence from Portugal.[415][416][414] After independence from Portugal in 1822, around 1.7 million Portuguese immigrants settled in Brazil.[414]
Portuguese immigration into Brazil in the 19th and 20th centuries was marked by its concentration in the states of São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. The immigrants opted mostly for urban centers. Portuguese women appeared with some regularity among immigrants, with percentage variation in different decades and regions of the country. However, even among the more recent influx of Portuguese immigrants at the turn of the 20th century, there were 319 men to each 100 women among them.[417] The Portuguese were different from other immigrants in Brazil, like the Germans,[418] or Italians[419] who brought many women along with them (even though the proportion of men was higher in any immigrant community). Despite the small female proportion, Portuguese men married mainly Portuguese women. Female immigrants rarely married Brazilian men. In this context, the Portuguese had a rate of endogamy which was higher than any other European immigrant community, and behind only the Japanese among all immigrants.[420]
Even with Portuguese heritage, many Portuguese-Brazilians identify themselves as being simply Brazilians, since Portuguese culture was a dominant cultural influence in the formation of Brazil (like many British Americans in the United States, who will never describe themselves as of British extraction, but only as "Americans", since British culture was a dominant cultural influence in the formation of The United States).
In 1872, there were 3.7 million Whites in Brazil (the vast majority of them of Portuguese ancestry), 4.1 million mixed-race people (mostly of Portuguese-African-Amerindian ancestry) and 1.9 million Blacks. These numbers give the percentage of 80% of people with total or partial Portuguese ancestry in Brazil in the 1870s.[421]
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a new large wave of immigrants from Portugal arrived. From 1881 to 1991, over 1.5 million Portuguese immigrated to Brazil. In 1906, for example, there were 133,393 Portuguese-born people living in Rio de Janeiro, comprising 16% of the city's population. Rio is, still today, considered the largest "Portuguese city" outside of Portugal itself, with 1% Portuguese-born people.[408][422]
Genetic studies also confirm the strong Portuguese genetic influence in Brazilians. According to a study, at least half of the Brazilian population's Y Chromosome (male inheritance) comes from Portugal. Black Brazilians have an average of 48% non-African genes, most of them may come from Portuguese ancestors. On the other hand, 33% Amerindian and 28% African contribution to the total mtDNA (female inheritance) of white Brazilians was found[423][424]
An autosomal study from 2013, with nearly 1300 samples from all of the Brazilian regions, found a predominant degree of European ancestry (mostly Portuguese, due to the dominant Portuguese influx among European colonization and immigration to Brazil) combined with African and Native American contributions, in varying degrees. 'Following an increasing North to South gradient, European ancestry was the most prevalent in all urban populations (with values from 51% to 74%). The populations in the North consisted of a significant proportion of Native American ancestry that was about two times higher than the African contribution. Conversely, in the Northeast, Center-West and Southeast, African ancestry was the second most prevalent. At an intrapopulation level, all urban populations were highly admixed, and most of the variation in ancestry proportions was observed between individuals within each population rather than among population'.[425]
A large community-based multicenter autosomal study from 2015, considering representative samples from three different urban communities located in the Northeast (Salvador, capital of Bahia), Southeast (Bambuí, interior of Minas Gerais) and South Brazilian (Pelotas, interior of Rio Grande do Sul) regions, estimated European ancestry to be 42.4%, 83.8% and 85.3%, respectively.[426] In all three cities, European ancestors were mainly Iberian.
It was estimated that around 5 million Brazilians (2.3% of the country's population) can acquire Portuguese citizenship, due to the last Portuguese nationality law that grants citizenship to grandchildren of Portuguese nationals.[427]
Oceania
[edit]Australia and New Zealand have sizeable Portuguese communities.

In Australia, although their numbers are relatively small in comparison to the Greek and Italian communities, the Portuguese constitute a highly organized, self-aware, and active community across various aspects of Australian life. Despite being among the early settlers, with some (unproven) theories that state they might have discovered Australia, their numbers have never been massive, when compared to major communities. The Portuguese immigration to Australia experienced a boom after the Carnation Revolution and the Indonesian Invasion of Timor-Leste. The Portuguese are dispersed throughout the country and engage in activities such as sports teams, social clubs, radio programs, newspapers, cultural festivals, culinary events, and even have a designated Portuguese neighborhood. The 73,903 people of Portuguese descent constitute about 0.28% of the Australian population. Portuguese cuisine has gained popularity within mainstream Australian society, exemplified by the rapid expansion and establishment of restaurants and fast-food outlets such as "Nando's", "Oporto," and "Ogalo." The delectable Portuguese pastry known as "pastel de nata" is widely enjoyed and readily available throughout the country. Many of the Portuguese are from Madeira.[428][429][430][431][432] Notable Portuguese Australians include Naomi Sequeira, Kate DeAraugo, Junie Morosi, Lyndsey Rodrigues, Sophie Masson and Irina Dunn.
The community in New Zealand is much smaller and the 1,500 Portuguese people living there (although the numbers could be significantly higher) constitute about 0.03% of the population. On 22 April 2010, the Office of Ethnic Affairs officially recognized Portuguese New Zealanders as a distinct community in New Zealand. A symbolic act of tying the 70th ribbon to Parliament's mooring stone in the Parliament House Galleria marked this recognition. In addition to their official recognition, the Portuguese community in New Zealand organizes various annual gatherings and celebrations, such as Portugal Day, and maintains a friendship association. Portuguese individuals were among the early settlers in New Zealand, although immigration from Portugal declined gradually until the 1960s. After the Carnation Revolution, the community started to increase again.[433][434]
In addition, about 900 Portuguese live in the French collectivity of New Caledonia (0.38% of the population).[435]
Asia
[edit]Portuguese influences are found throughout Asia, especially in Macau (see Macanese people), Timor-Leste and India (see Luso-Indian), all territories where the Portuguese maintained colonies up to the 20th century.[436][437]
Southeast Asia


Luso-Asian communities have had a strong presence in Southeast Asia since the 15th century. As a result of inter-ethnic marriage, dialects based on Portuguese have occurred in the former Portuguese territories now part of Malaysia (see Kristang people) and Singapore (see Eurasian Singaporeans). In particular, notable Kristang people from Malaysia include Kimberley Leggett, Jojo Sturys, Joan Margaret Marbeck, Elaine Daly, Nor Aliah Lee, Melissa Tan, Andrea Fonseka, Anna Jobling and Cheryl Samad. People of Portuguese descent from Singapore include personalities such as Pilar Arlando, Mary Klass and Vernetta Lopez.
Other communities are found in Indonesia (see Portuguese Indonesians and Mardjiker), with significant populations of Portuguese descent living in Lamno (the so-called "mata biru" or blue-eyed people), Aceh, Maluku Islands and Kampung Tugu.[438][439][440][441][442][443] Portuguese vestiges in Indonesia include dozens of loanwords as well as the introduction of Roman Catholicism (3.12% of the population but still the major religion in NTT) and Keroncong, similar to Portuguese cavaquinho.[444][445][446][447] In recent years many Indonesians of Portuguese descent have been active in the entertainment industry such as, among others, Puteri Indonesia Elfin Pertiwi Rappa or actress Millane Fernandez. In neighbouring Philippines, actress Sophie Albert is another example of Portuguese-South Asian working in the said industry.
Due to early Portuguese explorers, communities of Portuguese descent are also found in Myanmar (see Bayingyi people)[448][449] and Thailand (see Kudi Chin).[450][451] In Thailand, during the reign of King Narai the Great the Portuguese community in Ayutthaya is thought to have peaked at 6,000 people.[452] Notable Thai of Portuguese descent include Francis Chit, known for being the first Thai photographer, Maria Guyomar de Pinha, responsible for introducing Fios de ovos (or Foi Thong in Thai) and sangkhaya into Thai cuisine or actresses such as Kung Nang Pattamasuta, Krystal Vee or Neon Issara.
Indian Subcontinent


In Sri Lanka (see Burgher people, Portuguese Burghers and Mestiços), home to around 40,000 Burghers. A notable Portuguese Burger was the best-selling author Rosemary Rogers. In addition, as a consequence of the Portuguese invasion of Sri Lanka, during the 16th and 17th centuries, many Portuguese language surnames were adopted among the Sinhalese people. As a result, Perera and Fernando eventually became the most common names in Sri Lanka.[453][454][455] Afro Sri-Lankans also retain a Portuguese identity.[456] Major Portuguese contributions to Sri Lanka, dating to the colonial period, include, apart from archaeological vestiges, about 1,000 loanwords in Sinhala of Portuguese origin,[457] Baila music (from the Portuguese bailar, meaning to dance), culinary innovations such as "Bolo di amor" (literally Love cake) or "Bolo Folhado" (literally Puff Pastry)[458] as well as the introduction of Roman Catholicism (approximately 6.1% of the population identifies as Catholic) and the endangered Sri Lankan Portuguese creole.[459][460]
In Pakistan (see Portuguese in Pakistan) there is a small Portuguese community numbering about 64 people,[461] even though other estimates point at 400 people of Portuguese origin in Karachi alone.[462] Notable Portuguese Pakistani include actress Dilshad Vadsaria and scholar Bernadette Louise Dean. Despite today not being numerically visible[463] it is noteworthy to remember that, before the partition of India, it is estimated that the Goan community in Karachi numbered up to 15,000. The majority of them after 1947 moved back to Goa or went to other territories controlled by the Portuguese, as well as to the UK.[464] The Portuguese community has greatly contributed to the musical scene of the pre-1947 Karachi.[463] As of today, about 6,000 Goans remain in Pakistan, mainly in Karachi.[462]
Portuguese heritage is also present in Bangladesh, where they were the first Europeans to arrive:[465] not only did the Portuguese introduce Catholicism, a religion now professed by about 375,000 Bangladeshis,[466] but their heritage extends also to more than 1,500 words in Bengali that are of Portuguese origin.[467] In colonial times, the Portuguese population in Bangladesh may have reached 40,000 people[468][469] but, as time went by, many resettled to other colonies. Those who remained are now perfectly integrated in the larger Bangladeshi society. Notable examples of Portuguese influence in Bangladesh are the surnames bore by a large part of the Catholics, as well as Bangladesh's oldest church, the Holy Rosary Church in Dhaka.[470] As of now, the Portuguese community in Bangladesh is almost no existent with only a few expatriates[471] and some descendants of the early settlers.
Nevertheless, the most important Portuguese community found today in the Indian subcontinent – as well as in Asia as a whole when taking into account people with distant Portuguese ancestry – remains the one that has settled in India, especially in Goa, Damão e Diu and Dadrá e Nagar Aveli.[472]
East Asia

A small but growing Portuguese community – consisting mainly of recent expats and numbering about 3,500 people – is found in Japan,[473][474] South Korea,[475] China[476][477] and Taiwan, whose name used by European literature until the 20th century – Formosa, meaning "Beautiful (island)" - came from Portuguese.[478]
A 20,700 people-strong community also exists in Hong Kong, mainly of Macanese descent.[479] Notable people of Portuguese descent from Hong Kong include personalities such as Joe Junior, Michelle Reis, Rowan Varty, Rita Carpio and Ray Cordeiro.
Due to the shared past, the most important Portuguese community in Eastern Asia is the one in Macau, that was, until 1999, a Portuguese colony. With more than 150,000 Portuguese citizens, accounting for 22.34% of the total population, Portuguese influence in Macau is still very visible and Macau still has, as of today, the largest concentration of Portuguese nationals in Asia as well as one of the most important in the world.[480] Notable people from Macau of Portuguese descent include personalities such as singer Germano Guilherme.
List of countries by population of Portuguese heritage
[edit]Literature
[edit]
Portuguese literature has a long and varied history, with roots in the Middle Ages when troubadours dominated the literary world. In the 16th century, Portugal's literature entered its "Golden Age", during which time poets like Luís de Camões and Francisco de Sá de Miranda were some of the nation's most renowned literary figures.[607] Portuguese is often referred as to the "língua de Camões" (Camões's language), highlighting the importance the author had in forging the national identity as well as the domestic literary production.[608]
Famous Portuguese authors from the Age of Discoveries include Públia Hortênsia de Castro, Gomes Eanes de Zurara, Joana Vaz, Fernão Mendes Pinto (author of Peregrinação), Joana da Gama, Fernão Lopes and Violante do Céu.[609]
A new generation of authors appeared in the 19th century, including Almeida Garrett, who is credited with founding modern Portuguese literature. His writings reflect the political and social revolutions taking place in Portugal at the time, and his writing style is recognized as exceptionally original and unique for the time.[610]
Portuguese authors like Fernando Pessoa and Guerra Junqueiro gained international acclaim for their writings in the 20th century. In this century there was a great rise in the country's literary production. It is worth mentioning that Pessoa, due to him being considered very innovative and ground-breaking for his time, is often referred to as one of the most emblematic 20th-century Portuguese authors and his contributions to the nation's literary production are among the most notable ones.[611][612]
With modern authors like José Saramago and António Lobo Antunes, receiving both home and foreign critical recognition, Portuguese literature is still thriving today. These authors write about identity, culture, and society, and their writing reflects Portugal's rich and varied cultural legacy.
Notable Portuguese authors from the XIX centur onwards also include Ana Vicente, Richard Zimler, Ana Plácido, Mário Cesariny, Ana Hatherly, Cesário Verde, Isabel Stilwell, Miguel Torga, Ana de Castro Osório, Alves Redol, Maria Archer, Antero de Quental, Isabel Alçada, Wenceslau de Moraes, Vimala Devi, Alexandre Herculano, Dulce Maria Cardoso, Maria Gabriela Llansol, Abel Botelho, Fernanda Botelho, Isabel da Nóbrega, Rita Vilela, Maria Gabriela Llansol and Natália Correia. Dealing with contemporary poetry, notable figures include Matilde Campilho and Ana Daniel.
Moreover, Susan Lowndes Marques, writer and journalist, was a leading figure in the Portuguese-British community in Lisbon, and contributed to promoting Portugal in the UK. Still nowadays, with more than 2 million Britons coming to Portugal for their holidays every year, they are the most common international tourists in the country, second only to Spaniards.
Law and Justice
[edit]Portugal has not had as major of an impact on law and justice as some other Western countries, yet there have been famous Portuguese personalities over the years. Portugal created a legal system for its overseas possessions during the Age of Discovery, creating the basis for current international law. Another notable example is the 20th century, lawyer and diplomat José Cutileiro, who played a significant role in the negotiations that led to Portugal and Spain's entry into the European Union in 1986.
Particularly in the domain of human rights, Portugal has contributed significantly to the growth of international rights. The European Convention on Human Rights, which was established in 1950 with the purpose of defending human rights and basic freedoms, was one of the initiatives championed by Portugal, together with other EU countries, since its accession into the EU.
Notable Portuguese active in the field of Law and Justice include Paula Teixeira da Cruz (previous Minister of Justice), Boaventura de Sousa Santos GOSE (one of the most prominent Portuguese living left-wing intellectuals. ), Susana Amador, Henrique O'Neill, Maria Santos Pais (served as Special Representative of the United Nations Secretary-General on Violence against Children), Januário Lourenço (invented the Electronic Power of Attorney and the Electronic Divorce.), Isabel Oneto, Guilherme d'Oliveira Martins, Heloísa Apolónia and António Vitorino (former European Commissioner for Justice and Home Affairs).
Science and technology
[edit]In Portugal, research and development (R&D) units belong mainly to state universities and autonomous state research institutes carry out science and technology through a network. However, there are also non-state research institutes and some private projects.[613][614]
In the country's history the University of Lisbon, established in 1290 as a Studium Generale played a significant role. During the Age of Discovery a prime role was given to the study of technical requirements for navigation: clearly a topic of great importance in Portugal at this period, when control of sea trade was the primary source of Portuguese wealth. It was in this very period that major Portuguese contributions to the scientific world appeared, most notably the Caravel – a light and fast ship designed for coastal navigation and the Portolan – a maritime map used since the early Middle Ages for navigation. The Portuguese were also responsible for the introduction of the Compass rose on maps[615] and for the improvement of devices and techniques for guidance and navigation, such as the cross-staff.[616]
Other contributions include the nonius, the nautical astrolabe, the boat and the Black Maple Sword. During these times João Faras identified the Southern Cross while Francisco de Pina, in Asia, is credited for the invention of the modern Vietnamese alphabet (Quốc ngữ), often misattributed to French Alexandre de Rhodes.[617] In Viet Nam was also active botanist João de Loureiro.
In the 18th century, one of the oldest learned societies of Portugal, the Lisbon Academy of Sciences, was founded in 1779. During this time the Passarola was conceived. It was also during the 18th century that natural philosopher Jean Hyacinthe de Magellan was active and that Bento de Moura Portugal improved Thomas Savery's steam engine.
Within the Portuguese Empire, the Portuguese established in 1792 the oldest engineering school of Latin America (the Real Academia de Artilharia, Fortificação e Desenho), as well as the oldest medical college of Asia (the Escola Médico-Cirúrgica de Goa) in 1842.
During the late 19th century the Portuguese Bartolomeu de Gusmão introduced the Pyreliophore and Maximiliano Augusto Herrmann developed the Herrmann wall telephone. It was also the time in which spectrography pioneer Francisco Miranda da Costa Lobo and telectroscope pioneer Adriano de Paiva were active.
In 1949, the Portuguese neurologist António Egas Moniz, an early developer of the cerebral angiography, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
Modern contributions to the scientific community coming from Portugal include, among others, the drug Zebinix, the All-on-4 method (dentistry), the Multibanco, the Coloradd and the Prepaid mobile phone.
After WWII major Portuguese scientific and technical institutions emerged; among them is worth citing the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC) an international centre for biomedical research and founded by the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation (FCG) in 1961 and ranked as one of the Top Ten best Places for post-docs, by The Scientist – Faculty of 1000.
Other major instituitions include the Champalimaud Foundation, created at the bequest of Portuguese industrialist and entrepreneur, António de Sommer Champalimaud that focuses on the fields of neuroscience and oncology, and the International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory in Braga.
Despite its small size, In 2001 Portugal was ranked 28th among countries that contributed to the top 1% of the world's highly cited publications and Portugal was ranked 32nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2022.[618][619]
Within Europe and the European Union (EU), Portugal has full membership into several pan-European scientific organizations like the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Laboratory for Particle Physics (CERN), ITER, and the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Portuguese scientists and technicians work in all of those organizations. In the period 2005–2007, Portugal was the EU member state with the highest growth rate in research and development (R&D) investment as a percentage of the GDP – a 46% growth. Portugal's R&D investment equals 1.2% of Portuguese GDP. This was the 15th largest allocation of funds as a percentage of the GDP for R&D, among the 27 EU member states in 2007.[620]
Overall, the Portuguese contributed in numerous scientific fields. Some examples of notable Portuguese people who had made important contributions to science and technology, becoming in their time internationally known within their respective field, include:
- Agronomy (Alexandre Rodrigues Ferreira)
- Anthropology (Miguel Vale de Almeida, Jill Rosemary Dias, Leopoldina Ferreira Paulo, Teresa Joaquim)
- Astronomy (Paulo Freire)
- Astrophysics (David Sobral)
- Biochemistry (Sónia Rocha, Mónica Bettencourt-Dias, Helena Santos)
- Biology (Rolanda Matos)
- Botany (António Xavier Pereira Coutinho, Rosette Batarda Fernandes, Seomara da Costa Primo)
- Chemical engineering (Alírio Rodrigues, Isabel Gago, Armando J. L. Pombeiro)
- Chemistry (Roberto Duarte Silva, Branca Edmée Marques)
- Computer science (Diogo Vasconcelos, Fernando Boavida, Pedro Pedrosa Mendes, Isabel Cruz)
- Economics (Francisco Luís Gomes, Moisés Bensabat Amzalak, Rita Almeida, Lúcio Mauro Vinhas de Souza)
- Ethnology (António dos Santos Graça),
- Fluid dynamics (Silvana Cardoso)
- Geography (Orlando Ribeiro)
- Geology (Léon Paul Choffat, Venceslau de Lima, Carlos Ribeiro)
- Immunology (Benedita Barata da Rocha)
- Malariology (Maria Manuel Mota)
- Marine biology (Alexandra Cunha)
- Medical analysis (Mortó Sitarama Dessai)
- Metereology (Ilda Aurora Pinheiro de Moura Machado)
- Mycology (Mathilde Bensaude)
- Neuroscience (Megan Carey, Paula Isabel da Silva Moreira, Susana Lima, Ana Domingos, Hanna Damasio)
- Nuclear physics (Lidia Salgueiro)
- Paleontology (Miguel Telles Antunes)
- Pathology (Fátima Carneiro)
- Pharmaceutical Science (Luís Prista)
- Planning theory (Elisabete A. Silva)
- Primatology (Claudia Sousa)
- Protein Crystallography (Maria Arménia Carrondo)
- Psychology (Armindo Freitas-Magalhães, Ana Cristina Silva)
- Physics (José Mendes, Luís Amaral)
- Oncobiology (Raquel Seruca)
- Romance philology (Karoline Michaelis)
- Somnology (Teresa Paiva)
- Systems theory (Tessaleno Devezas)
- Theoretical physics (Pedro Vieira, João Penedones)
Other notable Portuguese scientists include:
- Corino Andrade – 20th century researcher author of the familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy's initial description
- Odette Ferreira – Portuguese professor of microbiology who played an important role in research on HIV, through the identification of the HIV-2
- Froilano de Mello – 20th century medical researcher and biologist
- Graça Freitas GCM – Director-General of Health who manages the strategies to be implemented against COVID-19 pandemic in Portugal.
- Diogo de Carvalho e Sampayo – amateur scientist from the 18th century who authored two important works on the subject of chromatics.
Moreover, due to the rich History of Portugal and the numerous civilisations that have inhabited the national territory, archaeology, first introduced by André de Resende in the 16th century, has been thoroughly studied. Among some of the Portuguese contributors to archaeology and historiography there are Estácio da Veiga, José Leite de Vasconcelos, Irisalva Moita, Luís Raposo, Samuel Schwarz, Miriam Halpern Pereira, Raquel Varelaand João de Barros. Manuel Valadares, pioneer in the use of X-rays for art restoration and paleoethnobotanist António Rodrigo Pinto da Silva also contributed to the study of Portuguese History.
Politics
[edit]Portuguese politics is defined within the framework of a parliamentary, representative multy-party democratic republic, where the Prime Minister is the head of government.
The president is the head of the country and has significant political power. He is elected for a 5-year term by direct vote, and he is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. His powers include the election of the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers, in accordance to general elections results. The Council of State, a presidential oversight body, is composed of six senior civilian officers, any former president elected since 1976, five members elected by the Assembly, and five directly appointed by the president.
The role of executive is assigned to the Council of Ministers. Both the Government and the Portuguese Parliament (Assembleia da República) are equipped with legislative rights. The Assembly is elected by universal suffrage under the system of proportional representation and deputies serve a four-year term. In case of extreme unrest or of impossibility of forming a government the president has the power to dissolve the Assembly and to call for new elections.
Since 1976, the Socialist Party (PS) and Social Democratic Party (PSD) have dominated the political landscape.
The judiciary in Portugal is independent of the executive and legislative branches and the national Supreme Court is the court of last appeal. Military, administrative and fiscal courts are designated as different court categories. A nine-member Constitutional Court verifies the constitutionality of legislation.
Economy
[edit]Portugal's economy is ranked 34th on the World Economic Forum's Global Competitiveness Report in 2019.[621]
The majority of international trade is with the EU, whose countries were the source and destination of more than 70% of Portugal's total international trade in 2020.[622] The total international trade amounted to approximately 153.3 billion Euros in 2022. Spain is by far, for evident historical and geographical reasons, the largest trading partner, accounting for 11.61% of exports and 32.07% of imports.[623][624] Other areas that are important trading partners with Portugal include NAFTA (6.3% of exports and 2% of imports), PALOP (5.7% of exports and 2.5% of imports), Maghreb (3.7% of exports and 1.3% of import and Mercosul (1.4% of exports and 2.5% of imports).
The Portuguese currency is the euro (€), which replaced the escudo in 2002 (that since 2022 is no longer exchangeable[625]) and the country has been part of the Eurozone since its foundation.
The country's national bank is Banco de Portugal, and it is part of the European System of Central Banks, and most of its trading takes place on Euronext Lisbon, owned by NYSE Euronext, the first global stock exchange.[626] Other important Portuguese banks include BES (now Novo Banco), CGD and Millennium BCP.
Portugal is home to a number of large companies with a great international reputation. Among the most renown Portuguese companies there is The Navigator Company, a major company in the international paper market; Sonae Indústria, the world's largest producer of wood panels; Corticeira Amorim, the world's largest producer of cork; Conservas Ramirez, the world's oldest producer of canned food; Cimpor, one of the world's 10 largest cement producers; EDP Renováveis, the world's third largest producer of wind energy; Jerónimo Martins, supermarket chains and market leader in Portugal, Poland and Colombia, José de Mello Group, one of the biggest Portuguese conglomerates, as well as TAP Air Portugal, which has a reputation for great safety and is one of the leading airlines in air transport between Europe, Africa and South America (especially Brazil) and Brisa - Autoestradas de Portugal.[627]
Other companies include Sumol + Compal, leader in the soft drink industry in Portugal and PALOP countries, Renova, a major company in tissue international market, Vista Alegre, a ceramics manufacturer established in 1824, Nelo (MAR Kayaks Ltda), a boat manufacturer, GestiFute, PR Portuguese company providing agent services for footballers. Also relevant are Pestana Group (tourism and leisure group) and Salvador Caetano.
In addition, there are many companies targeting the thriving media market, such as Impresa, Sociedade Independente de Comunicação (SIC), the first Portuguese private television network, NOS and MEO.
Education in Portugal has been gradually modernized and expanded since the 1970s. According to the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) in 2015, 15-year-old students in Portugal were significantly above the OECD average when it came to reading skills, mathematics and knowledge of science.[628][629] Portugal has several recognized universities and business schools that have contributed several well-known international leaders[630] and which attract an increasing number of foreign students. Portugal is both among the top senders and receivers country within the Erasmus+ programme,[631] with more student coming than leaving.[632]
Famous Portuguese businesswomen include Catarina Fagundes, CEO of Wind Birds, Catarina Portas, owner of A Vida Portuguesa, Fernanda Pires da Silva, President of Grupo Grão-Pará, a conglomerate focusing on construction, real estate, tourism, hotel management, and marble, Julia Carvalho, Corporate Manager at IBM, Maria da Conceição Zagalo, awarded by Amnesty International, as one of 25 women worldwide, "for her special dedication to social causes", Carla Castro and Eugénia Cândida da Fonseca da Silva Mendes.
On the other hand, Portuguese businessmen include Raul Pires Ferreira Chaves, inventor of a precursor to modern construction systems based on modular blocks, Paulo Maló, founder of Malo Clinic, Zeinal Abedin Mohamed Bava, António Miguel Ferreira, Paulo Morgado, currently Executive Vice-president of Capgemini Group, Henrique de Sommer, Fernando Van Zeller Guedes, co-founder of the international wine producer, Sogrape, and the inspiration behind the Mateus brand of rosé wine, Narciso Ferreira, Henrique de Mendonça, one of the protagonists of the economic phenomenon that saw the Portuguese colony of São Tomé and Príncipe turn into one of the world's main producers and exporters of cocoa in the early 20th century, Diogo Mónica, Portuguese-American entrepreneur and engineer who co-founded Anchorage Digital, a cryptocurrency and digital asset platform headquartered in the United States. Portuguese businessmen active abroad include Pedro José Lobo, a prominent member of the Macanese elite of the 20th century, Joe Berardo, Portuguese/South African entrepreneur, Arnaldo de Oliveira Sales, active in Hong Kong and José Filipe Torres, one of the 3 international experts on country branding and nation branding consultant.
Another notable Portuguese businessman is António Augusto Carvalho Monteiro, whose largesse created the Quinta da Regaleira.
Cuisine
[edit]
The oldest cookbook on Portuguese cooking comes from the 16th century and is titled Livro de Cozinha da Infanta D. Maria de Portugal[633] (Crown-Princess Maria's cookbook). It describes a number of well-known recipes made of beef, fish, fowl, and other traditional ingredients. Dating back to the High Middle Ages, agriculture had already a certain regional demarcation. There were both small peasant allotments and large latifundia. The latter are particularly characteristic of southern regions, which were annexed as a result of the Reconquista and distributed among the feudal lords, whereas further north, agricultural lots were usually smaller. In modern times, the cultivation of fruit and grapes began to play a particularly important role. Portugal is one of the world leaders in the production of strong red and dry white wines. Port wine and Madeira wine come from here. Portuguese farmers also grow pears, apples, plums, cherries, olives, citrus fruits and food crops such as wheat, rye, corn, oats, legumes.


Fishing is also an inherent occupation in Portugal, with sardines being caught from April to October. Both men and women work as fishermen.

Portuguese cuisine consists mostly on meats (pork, cattle, chicken and game among others), seafood (fish, crustaceans including lobster, crab, shrimp, prawns, and octopus), vegetables, legumes, and sweets (the most common of which are cakes). The Portuguese traditionally enjoy a diet rich in carbohydrates which often includes fresh breads like broa, rice, and potatoes with their meals.[634][635][636] The Portuguese are the Europeans recording the highest rice consumption per capita, eating 16.1 kg of rice per year, while the French eat 8.2 kg, Britons consume 7.4 kg and Poles eat around 3 kg.[637] Among Portuguese dishes using rice, Arroz de Tamboril (Monkfish rice), Arroz de Pato (duck rice) and Arroz de Cabidela (rooster rice) enjoy high popularity.[638] Consuming around 62 kg of potatoes per capita every year, the Portuguese are among the largest potato-consumers in the European Continent.[639] Portugal also has one of the largest livestock populations in the EU,[640] making meat very popular, and the very high fish-consumption being explained by the long 1,800 km of coastline (1,115 miles) which the country enjoys.
António-Maria De Oliveira Bello, also known as Olleboma, wrote "Culinária Portuguesa" (Portuguese Cuisine) in 1936.[641] Portuguese cuisine also draws from Mediterranean cuisine – Portugal is among the countries recognised by UNESCO for their Mediterranean diet – and cuisines from all over the world, especially from lands once part of the Portuguese Empire.
Starting in the 15th century,[642] Portugal played a pivotal global role in spice trade between the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies, particularly in the broad variety of spices used. These spices were also introduced to the Portuguese cuisine and are used in meat, fish, or several savory meals from mainland Portugal, the Azores, and the Madeira archipelago. They include piri piri (tiny, spicy chili peppers), white pepper, black pepper, saffron, paprika, clove, allspice, cumin, and nutmeg. Peri peri is so popular that Nando's, a South African multinational fast casual chain, operates over 890 outlets in 30 countries.[643] Their logo depicts the Rooster of Barcelos, one of Portugal's most common symbols.
In addition, numerous classic desserts and some savory meals contain cinnamon, vanilla, lemon, orange, anise, clove, and allspice. Portuguese merchants also introduced oranges in Middle Eastern countries. Today the Turkish ("Portakal"), Farsi (نارنجی or "portaqal") and Arabic (البرتقالي or "lburtuqaliiu") words for orange all denote a Portuguese origin. This term also extended to areas within the Ottoman Empire and beyond, today being used in languages such as Romanian (portocale), Albanian (portokalli), Greek (πορτοκάλι-portokáli) and Georgian (ფორთოხალი-portokhali).
A very popular dish is "Feijoada" where feijão is the Portuguese for bean. With feijoada salada de tomate and " vinagrete " or "molho vinagrete" are sometimes served. From a rich and varied cuisine, which includes a said 365 different ways of cooking cod (bacalhau), emblematic Portuguese traditional dishes are Cozido à portuguesa (Portuguese stew) and Caldo verde (green soup). The most globally widespread pastry is the pastel de nata, sometimes known as Natas or Portuguese custard tarts.
Portugal has 19 named wine regions Denominação de Origem Controlada with quality wines of controlled origin: Alenquer, Arruda, Bairrada, Beira Interior, Bucelas, Carcavelos, Colares, Dão, Douro, Encostas d'Aire, Lagoa, Lagos, Óbidos, Palmela, Portimão, Setúbal, Tavira, Távora-Varosa, Torres Vedras. The most famous Portuguese wine is 'Port' (Vinho do Porto), which may only be grown in the região demarcada do Douro, the Douro wines demarcated region. There are several unique types of Port wine, with an unchanging rich and intense bouquet, namely Porto Branco, Porto Ruby and Porto Tawny. Also famous, feature Vinho Verde[644] (green wine) slightly sparkling wine types, from the Minho region.
Famous Portuguese chefs include Filipa Vacondeus, Louise Bourrat[645] and Marlene Vieira.
Architecture
[edit]
Portuguese architecture encompasses the architectural styles and patrimony of Portugal and its former colonies, reflecting the artistic influences of diverse cultures throughout its rich history. The multiple civilizations that have inhabited Portugal or come in contact with its people have left their mark on its architecture, including the Romans and Moors. The Portuguese Empire's historical reach has led to a widespread heritage of Portuguese colonial architecture in many countries globally, particularly in Africa and the Americas, as well as Asia.
Epitomes of the Portuguese architectural style are Romanesque, Gothic and, above all, Manueline style. The Baroque and Rococo have had large usage in Portugal. After the 1755 Lisbon earthquake the Pombaline style (now candidate to become a listed UNESCO heritage site) took over and is still largely visible all over Portugal, especially in Portuguese Estremadura (the region of the capital city, Lisbon).



Over the centuries, various styles or movements have shaped Portuguese architecture, ranging from Romanesque to contemporary styles, and have produced celebrated architects such as Raul Lino, Fernando Távora and Álvaro Siza Vieira, among others.
Today, Portugal continues to produce talented architects, including Pritzker Architecture Prize winners Eduardo Souto de Moura and Siza Vieira, who have contributed to the ongoing evolution of Portuguese architecture. The Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian, built in the 1960s is one of the very best, defining examples of 20th-century Portuguese architecture.
In Portugal Tomás Taveira is also noteworthy, particularly due to stadium design. Other renowned Portuguese architects include Diogo de Arruda (who designed the well-known chapter house window at the Convent of Christ, in Tomar), Pedro Nunes Tinoco and Filippo Terzi (responsible for the Monastery of São Vicente de Fora), André Soares (who designed Falperra Church), José António Caldas (pioneer of the use of the dark room in Brazil), Carlos Amarante (who designed Bom Jesus do Monte), João Luís Carrilho da Graça, José da Costa e Silva (who established Neoclassical architecture in Portugal and colonial Brazil), José Luis Monteiro, João Abel Manta, Huguet and Mateus Fernandes (responsible for designing the Monastery of Batalha)
Famous architects from the 19th century include Maria José Marques da Silva, Helena Roseta, Miguel Ventura Terra and José Marques da Silva.
Portuguese architects who made contributions abroad include Alfredo Azancot working in Chile, Emanuele Rodriguez Dos Santos working in Italy, and Jo Palma working in Canada.
Music
[edit]
From folk music to classical, music has always played an important role in Portuguese culture.
Portuguese music is rich in history and cultural diversity. From traditional songs from the north of the country to the rhythms of Portuguese-influenced samba, from fado to Portuguese pop-rock, Portuguese music enjoys a centuries-long tradition.
The history of Portuguese music dates back to the country's foundation in the Middle Ages, when troubadours, poets and musicians, broadcast their love songs throughout the country.
In the 16th century, with the discovery of new lands and the expansion of the Portuguese Empire, new musical influences were introduced. One example is the famous stringed instrument, the Krencong, which was brought from Portugal to Indonesia and is one of the most notable Portuguese contributions to Indonesian culture still present today. Another instrument of Portuguese origin that is widely used in Hawaiian music today is the ukulele, with origins in Madeira Island.
Fado is, without a doubt, an emblematic musical genre of Portugal. Originating in Lisbon in the 19th century, it is considered a symbol of Portuguese culture. Fado songs often express love, saudade (longing) and difficulties in life. The great ambassador of Portuguese fado, Amália Rodrigues, had great success all over the world during the 1950s and 1960s. Today, musicians like Mariza, Ana Moura and Cristina Branco, Katia Guerreiro keep this musical art alive by modernizing it . The genre is one of two Portuguese music traditions in the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, with the other being Cante Alentejano.
Besides fado, the country has produced other forms of popular music, including Portuguese Pop Rock which developed in the 1980s and 1990s with artists such as Xutos & Pontapés, Rui Veloso and the Madredeus. The band Madredeus have been noted for their innovative use of the Portuguese guitar, a traditional Portuguese instrument.

Other popular modern multicultural genres in Portugal include dance, house, kizomba, pimba, pop, reggae, ska and zouk.
In Portugal we can also find famous names in world music, such as the musician Waldemar Bastos. With his exceptional voice, he conquered international stages and worked with renowned musicians such as Peter Gabriel.
In conclusion, Portuguese music is rich and diverse, offering a multitude of different styles that deserve to be discovered. Whether with fado, pop rock or classical music, the Portuguese contribution to world music is undeniable. Portuguese musical heritage – as is the case with musical traditions from all over the world – is a musical gem that must be preserved for future generations.
A notable Portuguese kizomba author is Soraia Ramos. Dealing with Rap, Ângelo César do Rosário Firmino and Diana De Brito are important names within the Portuguese musical scene.
Hip hop began in Portugal in the early 1990s. The first artist to sign a major record deal was General D with EMI Records. Other important artists from the Hip hop tuga genre include Sam the Kid and Regula.
In jazz, notable Portuguese performers include Carmen Souza, Marta Dias, Vânia Fernandes, Maria João and Luísa Sobral. while in the kuduro musical genre in Portugal Keidje Torres Lima is notable. Other authors include names such as Lura, Georgina Ribas, Filipa Azevedo, Nenny, Ana Free, Ana Bela Alves and Bárbara Bandeira.
Cinema
[edit]Portuguese cinema is a popular art that has grown and evolved over the years. It appeared at the end of the 19th century, with the screening of silent films in music halls and theatres. However, it was not until the 1920s that cinema became an important cultural and artistic element in Portugal.
The first Portuguese film, shot in Porto, was directed by Aurélio da Paz dos Reis in 1896. In homage to the Departure of the Workers from the Lumière Factory (La Sortie de l'usine Lumière à Lyon) by Auguste and Louis Lumière shot in 1895, he filmed the Departure of the Workers from the Confiança Factory (Saída do Pessoal Operário da Fábrica Confiança).[646]
José Leitão de Barros pioneered the Portuguese film industry, producing and directing several silent films starting in the 1910s.[646] One of the first notable Portuguese female actresses is Cremilda de Oliveira. Portuguese director Manoel de Oliveira extended de la Velle's legacy. His film "Aniki-Bóbó" (1942), remains a major Portuguese film for its innovation and poetic vision of adolescence. Manoel de Oliveira has made more than 30 films, including his last, "I'm Going home" (2001), produced at the age of 93.
In the 1950s, new American technologies gave a resurgence of interest in Hollywood films rather than those from Portugal. In the 1960s, with the international cultural opening, the attention of the Portuguese public was brought back to national soil. The 1960s saw the rise of innovative cinema, notably with director Fernando Lopes. He made films that touched on the themes of politics and religion, generating debate and great controversy at the time. His film "Belarmino" (1964), won the Golden Lion at that year's Venice exhibition.
Fernando Lopes paved the way for a new generation of directors who continued to be active in the 70s and 80s. This period saw films like "Mudar de Vida" (1966) by Paulo Rocha. Moreover, it was in the 70s that The School of Reis – a film theory concept relative to the teachings of Portuguese director António Reis and Margarida Cordeiro – emerged. Notable authors influenced by Reis are João Pedro Rodrigues and Pedro Costa.[647]
Despite their national success, Portuguese films have often been ignored by international festivals. However, this has started to change with the emergence of some very talented directors such as Marco Martins.
In 1989, the first of a new wave of filmmakers, Pedro Costa, presented "O Sangue". This film, along with its follow-up efforts in the 90s, 'Ossos' and 'Casa de Lava ', shaped a style that would gradually gain international recognition. Costa became a creator of films in competition at Cannes.
Portuguese directors have also played an increasingly important role in the international film industry. Director Manoel de Oliveira was the first Portuguese director to compete for the Palme d'Or at Cannes in 1985. Since then, several other renowned Portuguese filmmakers have competed at major international festivals. Cinema has evolved over time and Portugal has not been left out with the changes that are happening in the field. Portuguese directors have continued to produce films close to their audiences while opening them up to foreign countries.
Telenovela is a popular genre in Portugal, especially due to the Brazilian influence, and the country is a major producer and consumer of telenovelas in the Portuguese-speaking world.[648][649] Many Portuguese telenovelas have reached international fame, such as A Única Mulher, Floribella, Morangos com Açúcar, Laços de Sangue or Conta-me como foi. Major networks producing multiple telenovelas every year include SIC and TVI. Notable telenovela actors include Liliana Santos, Lúcia Moniz, Diogo Morgado, Vera Kolodzig, Sílvia Alberto, Diogo Amaral, Rita Pereira, Joana Ribeiro, Ricardo Pereira, Mariana Monteiro, Luciana Abreu.
Many Portuguese authors, in addition, have participated in international productions; among them Daniela Melchior, Nuno Lopes, Cris Huerta, Helena D'Algy and Rafael Morais.
Among the many actors, producers and entertainers that have emerged from Portugal one ought to remember Nuno Sá Pessoa and Diana Andringa for documentaries, famous TV hosts Nuno Markl, Rita Camarneiro, Ricardo Araújo Pereira, Filomena Cautela and Eduardo Serra, best known for his work on the final two Harry Potter films, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 1 and Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2. Other names include polyedric Suspiria Franklyn and first female director Bárbara Virgínia.
Ultimately, Portuguese cinema has contributed enormously to the artistic and cultural expression of Portugal as well as to world cinema. Directors have been and remain great artists and the legacy they left represents a tremendous contribution to the cinematic arts.
Influencers (Instagram)
[edit]This is a list of the top 10 accounts managed by Portuguese nationals (Brand accounts excluded) with most followers on the photo and video-sharing social platform Instagram.[650][651][652] Instagram is, as of 2023, one of the most popular social media platforms in Portugal,[653][654] as well as in the whole world.[655][656]
The most followed individual is Portuguese footballer Cristiano Ronaldo who is, as well, the most followed person on Instagram overall. Because of the large Portuguese diaspora, of the 10 most followed Portuguese people (defined as holding a Portuguese passport) 7 were owned by Luso-Brazilian citizens.
| Rank | Username | Owner | Followers |
Profession/Activity | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | @cristiano | Cristiano Ronaldo | 622,000,000 | Footballer | Most followed person on Instagram | |
| 2 | @virginia | Virginia Fonseca | 46,000,000 | Influencer, YouTuber, businesswoman | American-born Brazilian who also holds Portuguese nationality. This makes her the most followed Portuguese woman on Instagram.[657] | |
| 3 | @gioewbank | Giovanna Ewbank | 29,300,000 | Actress, model, Television presenter | Brazilian-born Luso-Brazilian citizen[658] | |
| 4 | @phil.coutinho | Philippe Coutinho | 24,400,000 | Footballer | Most followed Brazilian-born Luso-Brazilian man on Instagram[659] | |
| 5 | @brunogagliasso | Bruno Gagliasso | 22,300,000 | Actor | Luso-Brazilian citizen[658] | |
| 6 | @official_pepe | Pepe | 17,600,000 | Footballer | Brazilian-born | |
| 7 | @felipeneto | Felipe Neto | 17,300,000 | YouTuber | Luso-Brazilian citizen[660] | |
| 8 | @ileana_official | Ileana D'Cruz | 16,400,000 | Actress | Indian-born | |
| 9 | @joaofelix79 | João Félix | 11,800,000 | Footballer | ||
| 10 | @brunofernandes8 | Bruno Fernandes | 8,800,000 | Footballer | ||
| As of February 26, 2024[update] | ||||||
Among positions 11 to 50 of the list of the most followed Portuguese citizens on social media platform Instagram, one can notice the large number of footballers. In fact, football is arguably the most popular sport in Portugal.
| Rank | Username | Owner | Followers |
Profession/Activity | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | @oficialkellykey | Kelly Key | 8,700,000 | Singer | Luso-Brazilian citizen[661] | |
| 12 | @sarasampaio | Sara Sampaio | 8,600,000 | Model | Most followed Portuguese-born Portuguese model on Instagram | |
| 13 | @jpcancelo | João Cancelo | 6,800,000 | Footballer | ||
| 14 | @pedroscooby | Pedro Scooby | 5,800,000 | Surfer | Luso-Brazilian[662] | |
| 15 | @luccasneto | Luccas Neto | 5,800,000 | Actor, comedian | Luso-Brazilian[663] | |
| 16 | @iamrafaeleao93 | Rafael Leão | 5,600,000 | Footballer | Being of Portuguese-Angolan descent, he is the most followed Luso-African on Instagram | |
| 17 | @ederson93 | Ederson Moraes | 5,200,000 | Footballer | Luso-Brazilian[664] | |
| 18 | @luis__figo | Luís Figo | 4,900,000 | Footballer | ||
| 19 | @renatosanches18 | Renato Sanches | 4,800,000 | Footballer | Of São Tomé and Príncipe and Cape Verdean descent | |
| 20 | @bernardocarvalhosilva | Bernardo Silva | 4,700,000 | Footballer | ||
| 21 | @doloresaveiroofficial | Dolores Aveiro | 4,300,000 | Cristiano Ronaldo's mother | ||
| 22 | @josemourinho | José Mourinho | 4,100,000 | Football manager | ||
| 23 | @ricardoquaresmaoficial | Ricardo Quaresma | 4,100,000 | Footballer | Most followed Portuguese of Romani descent | |
| 24 | @rubendias | Rúben Dias | 3,600,000 | Footballer | ||
| 25 | @diogodalot | Diogo Dalot | 3,100,000 | Footballer | Most followed Portuguese of French descent on Instagram | |
| 26 | @nelsonsemedo50 | Nélson Semedo | 3,000,000 | Footballer | Of Cape Verdean descent | |
| 27 | @jorgejesus | Jorge Jesus | 3,000,000 | Football manager | ||
| 28 | @luisnani | Nani | 2,500,000 | Footballer | Of Cape Verdean descent | |
| 29 | @ferodriguesoficial | Fernanda Rodrigues | 2,300,000 | Actress, Television presenter | Luso-Brazilian[665] | |
| 30 | @diogoj_18 | Diogo Jota | 2,300,000 | Footballer | ||
| 31 | @fabio_coentrao | Fábio Coentrão | 2,000,000 | Footballer | ||
| 32 | @aftgomes21 | André Gomes | 1,800,000 | Footballer | ||
| 33 | @magui_corceiro | Margarida Corceiro | 1,800,000 | Actress | Most followed Portuguese born in the 21st century | |
| 34 | @andresilva9 | André Silva | 1,500,000 | Footballer | ||
| 35 | @dailycristina | Cristina Ferreira | 1,600,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 36 | @hyndia | Rita Pereira | 1,500,000 | Actress | ||
| 37 | @pedrocarvalho_oficial | Pedro Carvalho | 1,500,000 | Actor | Most followed Portuguese male actor | |
| 38 | @katiaaveirooficial | Kátia Aveiro | 1,400,000 | Pop singer | ||
| 39 | @explorerssaurus_ | Raquel e Miguel | 1,300,000 | Travellers | Most followed Portuguese couple on Instagram | |
| 40 | @danielamelchior | Daniela Melchior | 1,300,000 | Actress | ||
| 41 | @ricardinho10oficial | Ricardinho | 1,300,000 | Futsal player | Most followed Portuguese futsal player | |
| 42 | @h.herrera16 | Héctor Herrera | 1,200,000 | Footballer | Most followed Portuguese citizen of Mexican descent on Instagram | |
| 43 | @sergioliveira27 | Sérgio Oliveira | 1,200,000 | Footballer | ||
| 44 | @iamdanilopereira | Danilo Pereira | 1,200,000 | Footballer | Most followed Guinea-Bissau born Portuguese on Instagram | |
| 45 | @claudiavieiraoficial | Cláudia Vieira | 1,200,000 | Actress, Television presenter | ||
| 46 | @pedrobarrosopb | Pedro Barroso | 1,100,000 | Actor | ||
| 47 | @nunomendes | Nuno Mendes | 1,100,000 | Footballer | Of Angolan descent | |
| 48 | @rubendsneves | Rúben Neves | 1,100,000 | Footballer | ||
| 49 | @gonolivier | Gonçalo Olivier | 1,100,000 | Influencer | One of the most followed Portuguese influencers[666][667] | |
| 50 | @danielaruah | Daniela Ruah | 1,100,000 | Actress | Most followed American-Bissau born Portuguese on Instagram | |
| As of February 26, 2024[update] | ||||||
Ranking 51–100 in the list of most followed Portuguese on Instagram there are many actresses and Television personalities. Although the numbers may seem low, they are important when compared to the population of Portugal. Giving that people in the following table are mostly known in the domestic market, an Influencer with 800,00 followers, for example, reaches out to 7.6% of the Portuguese people (if taking into account also approximately 5 million people in the Portuguese diaspora holding Portuguese nationality, they reach 5.3% of the Portuguese nationals worldwide).
| Rank | Username | Owner | Followers |
Profession/Activity | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 | @daniellapintto | Daniela Pinto Scuderi | 1,100,000 | Social media personality | Most followed member of the Portuguese diaspora in Switzerland[668] | |
| 52 | @sofiarribeiro | Sofia Ribeiro (actress) | 1,100,000 | Actress | ||
| 53 | @jessica_athayde | Jessica Athayde | 1,000,000 | Model | Most followed Portuguese of British descent on Instagram | |
| 54 | @kellybaileyy | Kelly Bailey | 1,000,000 | Actress | Of British descent | |
| 55 | @davidcarreiraoficial | David Carreira | 1,000,000 | Model, Singer | Most followed French-born Portuguese on Instagram | |
| 56 | @carolinadeslandes | Carolina Deslandes | 1,000,000 | Singer | ||
| 57 | @nellyfurtado | Nelly Furtado | 1,000,000 | Singer | Canadian-born | |
| 58 | @saramatosofficial | Sara Matos | 1,000,000 | Actress | ||
| 59 | @miguelpaixao7 | Miguel Paixão | 1,000,000 | Footballer | ||
| 60 | @ibeneizergirosa7 | Ibineizer Giro Sá | 1,000,000 | Model | Of Guinea-Bissau descent, he is the most followed Afro-Portuguese fashion model on Instagram | |
| 61 | @soraiaramoss | Soraia Ramos | 996,000 | Singer | Most followed Portuguese singer of Cape Verdean descent on Instagram | |
| 62 | @deco_official | Deco | 987,000 | Footballer | Luso-Brazilian | |
| 63 | @otaviomonteiroo | Otávio Monteiro | 987,000 | Footballer | Brazilian-born | |
| 64 | @yasmine_official_ | Yasmine | 987,000 | Singer | Of mixed Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verdean descent[669] | |
| 65 | @barbarabandeiraa | Bárbara Bandeira | 983,000 | Singer | ||
| 66 | @deborasofiabatista | Debora Batista | 975,000 | Model | ||
| 67 | @carolinapatrocinio | Carolina Patrocínio | 972,000 | TV host | ||
| 68 | @irisloveunicorns | Inês Silva | 966,000 | YouTuber | ||
| 69 | @lourencoortigao | Lourenço Ortigão | 964,000 | Actor | ||
| 70 | @raminhoseffect | António Raminhos | 957,000 | Comedian | Known for Missão: 100% Português | |
| 71 | @ricardotpereira | Ricardo Pereira | 947,000 | Actor | ||
| 72 | @gedson_83 | Gedson Fernandes | 943,000 | Footballer | São Tomé and Príncipe-born | |
| 73 | @the_naturalcoach | André Carvalho | 928,000 | Coach | Most followed Portuguese coach | |
| 74 | @rpatricio1 | Rui Patrício | 925,000 | Footballer | Most followed Portuguese goalkeeper | |
| 75 | @mlgoucha | Manuel Luis Goucha | 920,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 76 | @dichavesofficial | Diana Chaves | 919,000 | Actress | ||
| 77 | @vitinha | Vitinha | 915,000 | Footballer | ||
| 78 | @pedroteixeiraoficial | Pedro Teixeira (actor) | 908,000 | Actor | ||
| 79 | @calema507 | Calema | 895,000 | Musical duo | Of São Tomé and Príncipe descent; most followed musical duo in Portugal | |
| 80 | @wuant | Wuant | 890,000 | Singer | ||
| 81 | @apipocamaisdoce | Ana Garcia Martins | 888,000 | Blogger | Most followed Portuguese blogger | |
| 82 | @angelorodrigues_oficial | Ângelo Rodrigues | 885,000 | Actor | ||
| 83 | @raphaelguerreiro14 | Raphaël Guerreiro | 881,000 | Footballer | French-born | |
| 84 | @angeladscosta | Angie Costa | 877,000 | Artist | ||
| 85 | @nunomarkl | Nuno Markl | 873,000 | Comedian, Radio Host, writer | Most followed Portuguese of Austrian descent | |
| 86 | @cesartmourao | César Mourão | 866,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 87 | @odeith | Sérgio Odeith | 865,000 | Artist | Artist known for his murals[670] | |
| 88 | @88migueloliveira | Miguel Oliveira | 856,000 | Racing driver | Most followed Portuguese racing driver on Instagram | |
| 89 | @caroloureiro | Carolina Loureiro | 842,000 | Actress | ||
| 90 | @alba.baptista | Alba Baptista | 841,000 | Actress | ||
| 91 | @o_unas | Rui Unas | 827,000 | TV personality, actor, YouTuber | ||
| 92 | @lilianafilipa__ | Liliana Filipa | 809,000 | Businesswoman, Influencer | ||
| 93 | @windoh | Diogo da Silva | 806,000 | YouTuber | ||
| 94 | @fatimalopesoficial | Fátima Lopes (presenter) | 795,000 | Television personality | ||
| 95 | @kazzio7 | SirKazzio | 792,000 | YouTuber, Singer | Most followed Luso-Venezuelan on Instagram | |
| 96 | @joaopalhinha6 | João Palhinha | 792,000 | Footballer | ||
| 97 | @catarinafurtadooficial | Catarina Furtado | 763,000 | Actress, Television presenter | She is an UNFPA Goodwill Ambassador | |
| 98 | @cedricsoares41 | Cédric Soares | 761,000 | Footballer | German-born | |
| 99 | @joaomoutinho8 | João Moutinho | 760,000 | Footballer | ||
| 100 | @corpodormente | Bruno Nogueira | 752,000 | Humorist, actor, Television host | ||
| As of February 26, 2024[update] | ||||||
In positions 101–150 of the most followed Portuguese on Instagram there are many actresses as well as well known television personalities popular with Portuguese public.
| Rank | Username | Owner | Followers |
Profession/Activity | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | @trincao | Francisco Trincão | 751,000 | Footballer | ||
| 102 | @ccosta99 | Cassie Costa | 750,000 | Model | ||
| 103 | @helenacoelhooo | Helena Coelho | 740,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 104 | @elma_oficial | Elma Aveiro | 729,000 | Businesswoman | She is Cristiano Ronaldo's sister | |
| 105 | @tonycarreiraoficial | Tony Carreira | 724,000 | Singer | ||
| 106 | @goncaloramos88 | Gonçalo Ramos | 724,000 | Footballer | ||
| 107 | @oceanabasilio | Oceana Basilio | 720,000 | Actress, model | ||
| 108 | @jesustecatitoc | Jesús Manuel Corona | 706,000 | Footballer | Of Mexican descent | |
| 109 | @vera.von.monika | Vera Von Monika | 705,000 | Businesswoman, model | ||
| 110 | @jessiicasilva10 | Jéssica Silva | 696,000 | Footballer | ||
| 111 | @joaomario | João Mario | 688,000 | Footballer | Of Angolan descent | |
| 112 | @anaguiomar.oficial | Ana Guiomar | 684,000 | Actress | ||
| 113 | @filomenacautela | Filomena Cautela | 681,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 114 | @danianeto | Dânia Neto | 680,000 | Actress | ||
| 115 | @iamisabelsilva | Isabel Silva | 680,000 | Athlete | ||
| 116 | @djdiegomiranda | Diego Miranda | 678,000 | Dj | Most followed Portuguese Dj on Instagram | |
| 117 | @nininhovazmaia_ | Nininho Vaz Maia | 656,000 | Singer | ||
| 118 | @maryyy_monteiro | Mariana Monteiro | 653,000 | Actress, model | ||
| 119 | @diogopicarra | Diogo Piçarra | 645,000 | Singer | ||
| 120 | @categouveia | Catarina Gouveia | 639,000 | Actress | ||
| 121 | @rochacomedy | Fernando Rocha | 634,000 | Comedian | ||
| 122 | @mrjasonsantos | Jason Santos | 634,000 | Pr | ||
| 123 | @vanesssamartins | Vanessa Martins | 625,000 | Actress | ||
| 124 | @fernandodaniel | Fernando Daniel | 623,000 | Singer | ||
| 125 | @brunosavateoficial | Bruno Savate | 617,000 | Television personality | ||
| 126 | @_fabio.10 | Fabio Carvalho | 616,000 | Footballer | Of Angolan descent, most followed Portuguese from Marvila | |
| 127 | @claudio_ramos | Cláudio Ramos | 615,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 128 | @ricardoweezy | Ricardo Teles | 613,000 | Video creator | ||
| 129 | @_saraprata_ | Sara Prata | 610,000 | Actress, model | ||
| 130 | @tania_m0reira | Tânia Moreira | 604,000 | Influencer | ||
| 131 | @marcocosta22 | Marco Costa | 598,000 | Chef | ||
| 132 | @bernardorsousa | Bernardo Sousa | 593,000 | Rally driver | ||
| 133 | @madalena_abecasis | Madalena Abecasis | 580,000 | Designer | ||
| 134 | @mariabotelhomoniz | Maria Botelho Moniz | 580,000 | Actress, Television presenter | ||
| 135 | @mafalda.sampaio | Mafalda Sampaio | 580,000 | Model | ||
| 136 | @vanessabarragao_work | Vanessa Barragão | 579,000 | Artist | Most followed Portuguese female artist on Instagram | |
| 137 | @sofiaarrudagram | Sofia Arruda | 575,000 | Actress, model | ||
| 138 | @bumbanafofinha | Mariana Cabral | 575,000 | Blogger, comedian | ||
| 139 | @asnove | Sofia de Castro Fernandes | 565,000 | Blogger | ||
| 140 | @joana____duarte | Joana Duarte | 555,000 | Actress | ||
| 141 | @gustavoribeiro | Gustavo Ribeiro | 550,000 | Skateboarder | Most followed Portuguese skateboarder on Instagram | |
| 142 | @daniel__oliveira | Daniel Oliveira (Television presenter) | 544,000 | Television presenter | ||
| 143 | @carlosqueiroz_ | Carlos Queiroz | 540,000 | Football manager | ||
| 144 | @itsfannyrodrigues | Fanny Rodrigues | 534,000 | Television personality | Swiss-born[671] | |
| 145 | @carol_carvalhosantos | Carolina Carvalho | 533,000 | Actress | ||
| 146 | @ines_ap | Inês Aires Pereira | 533,000 | Actress | ||
| 147 | @goncaloguedes17 | Gonçalo Guedes | 531,000 | Footballer | ||
| 148 | @eduardo.madeira8 | Eduardo Madeira | 524,000 | Actor | ||
| 149 | @vascopalmeirim | Vasco Palmeirim | 517,000 | Television presenter | Most followed Portuguese-born of Goan descent[672] | |
| 150 | @mrkevensantos | Keven Santos | 516,000 | Actor | US-born[673] | |
| As of February 26, 2024[update] | ||||||
See also
[edit]- Ethnic groups in Europe
- Galicians
- Luso-Asians
- Luso-Africans
- Iberian Jews
- Portuguese American
- Portuguese Canadians
- List of Portuguese people
- Portuguese cuisine
- Portuguese culture
- Lusitanics
- Lusophone
- Portuguese language
- Category:Portuguese people
Notes
[edit]- ^ Only people legally registered as living in Portugal and not holding Portuguese nationality (thus excluding naturalised citizens and descendants of immigrants) are taken into account. For further information see Immigration to Portugal
References
[edit]- ^ "População residente ultrapassa os 10,6 milhões - 2023". ine.pt. INE. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Estudo descobre 31,19 milhões de portugueses pelo mundo". Dn.pt. Archived from the original on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ "Relations bilatérales avec le Portugal et France". France Diplomatie : : Ministère de l'Europe et des Affaires étrangères. Archived from the original on 15 December 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ a b c d Glaser, Clive (2013). "The Making of a Portuguese Community in South Africa, 1900–1994". Imperial Migrations. pp. 213–238. doi:10.1057/9781137265005_9. ISBN 978-1-349-34604-2.
- ^ "A Lisbonne, une visite d'Elisabeth Borne dédiée à la culture et aux dossiers énergétiques". 29 October 2022.
- ^ "Portuguese Americans are organized and well connected". 13 April 2011.
- ^ ""Nós unimos, não dividimos, nós criamos a paz, não a guerra"". 11 June 2018.
- ^ "TVI Internacional disponível para 1 milhão e 400 mil portugueses nos EUA". 15 July 2013.
- ^ "Ministro de Portugal discutiu crise na Venezuela "todos os dias" na Assembleia Geral". News.un.org. 26 September 2019.
- ^ "Maior comunidade portuguesa da América Latina esperançada numa nova Venezuela". Jn.pt. 13 April 2013.
- ^ a b "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Venezuela". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Crisis has Venezuela's Portuguese returning to roots". France 24. 6 February 2019.
- ^ "Reforço consular em países à volta da Venezuela". Publico.pt. 8 December 2019.
- ^ "Ethnic or cultural origin by gender and age: Canada, provinces and territories". 26 October 2022.
- ^ "Os passos tímidos da língua portuguesa no Canadá". 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Esquema relacionado com burla na imigração está a preocupar portugueses no Canadá". 10 January 2016.
- ^ ""Portugueses no Canadá são embaixadores de Portugal"".
- ^ a b "José Eduardo dos Santos diz que trabalhadores portugueses são bem-vindos em Angola". Observatório da Emigração. Archived from the original on 20 September 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
...presença de cerca de 200 mil trabalhadores portugueses no país...
- ^ Rausa, Fabienne; Reist, Sara (2008). Ausländerinnen und Ausländer in der Schweiz: Bericht 2008 [Foreigners in Switzerland: Report 2008] (PDF) (in German). Neuchâtel: Swiss Federal Statistical Office. p. 16. ISBN 978-3-303-01243-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 August 2013. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ Afonso, Alexandre (2015). "Permanently Provisional. History, Facts & Figures of Portuguese Immigration in Switzerland". International Migration. 53 (4): 120–134. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2435.2010.00636.x. S2CID 143290940.
- ^ a b "Observatório da Emigração-Suíça". Observatorioemigracao.pt. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Alemanha". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses em Moçambique". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ Glaser, Clive (2013). "The Making of a Portuguese Community in South Africa, 1900–1994". The Making of a Portuguese Community in South Africa, 1900–1994, pag. 213–238. Migration, Diasporas and Citizenship. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 213–238. doi:10.1057/9781137265005_9. ISBN 9781137265005.
- ^ Ojeda, Luis Thayer (1989). "origenes de chile:elementos etnicos, apellidos, familas".
- ^ "Estadística de extranjeros residentes en España".
- ^ "Population of the United Kingdom by country of birth and nationality, July 2020 to June 2021". ons.gov.uk. Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 3 January 2024. Retrieved 5 February 2023..
- ^ "Brexit: Portugueses no Reino Unido desesperam para renovar documentos".
- ^ "Portugueses no UK". 13 September 2022.
- ^ "Parlamento de Portugal sobre portugueses no UK" (PDF).
- ^ "UK-Portuguese Newspaper Launched in Thetford Norfolk".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses em Macau". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses no Luxemburgo". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Mianmar. A terra em que houve reis portugueses".[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Casas incendiadas, terror e morte em Myanmar: Luso-descendentes católicos Bayingyi no alvo dos militares".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Índia". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Bélgica". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Há portugueses que admitem "renunciar à nacionalidade" devido à burocracia nos consulados belgas". Expresso.pt.
- ^ "Fact sheet – Ancestry". Abs.gov.au.
- ^ "Cultural diversity: Census". Abs.gov.au. 12 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Expresso". Jornal Expresso. Archived from the original on 10 December 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ^ "Buenos Aires celebra Portugal".
- ^ "Los portugueses del Buenos Aires tardocolonial:Inmigración, sociedad, familia, vida cotidiana y religión" (PDF).
- ^ "Minhotos na Argentina celebram Portugal".
- ^ "10 de Junho: Instituições na Argentina celebram em conjunto pela 1.ª vez". 10 June 2020.
- ^ "Povo Burgher – Quem são? Como surgiram? História e Formação". 9 August 2019.
- ^ "Malaysia, Singapore & Brunei travel". Lonelyplanet.com.
- ^ Jarnagin, Laura (2012), Portuguese and Luso-Asian Legacies in Southeast Asia, 1511–2011: Culture and identity in the Luso-Asian world, tenacities & plasticities. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies., p. 268
- ^ "Papiá Kristang".
- ^ "Uma história da língua" (PDF).
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses nos Países Baixos". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses em Timor-Leste". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Portugal apela a estudantes portugueses em Hong Kong que enviem dados pessoais para receberem apoio".
- ^ "Comunidades Portuguesas no Mundo". Archived from the original on 7 October 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "People of Malawi".
- ^ "People of Zimbabwe".
- ^ "Palabra-palabra di pasadu". 23 April 2018.
- ^ "About Kristang". 17 June 2016.
- ^ "Kodrah Kristang: The initiative to revitalize the Kristang language in Singapore".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses em Andorra". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Relações Bilaterais Portugal-Andorra". Portaldiplomatico.gov.mne.pt.
- ^ "The History of the Portuguese in Bermuda". 29 April 2021.
- ^ "The Bermuda Census". Gov.bm. 2 March 2016.
- ^ "Marco tem "dinheiro fresco" na Bermuda, mas sente falta da gastronomia açoriana".
- ^ "Associação prepara livro histórico sobre presença portuguesa nas Bermudas".
- ^ "Escola de português nas Bermudas procura acreditação junto do instituto Camões".
- ^ "Emigrantes nas Bermudas deixam de visitar Portugal por não poderem conduzir no país".
- ^ "Associação dos Emigrantes Açorianos foi às Bermudas para registar História de 175 anos de presença portuguesa". Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "2021 Jersey census" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 April 2022. Retrieved 19 May 2022.
- ^ "Clubes desportivos dão vida e visibilidade à comunidade portuguesa em Jersey".
- ^ "Fluxo começou na década de 50". 28 November 2005.
- ^ ""Nossa moeda é a fé": Como uma igreja impediu que um templo virasse um restaurante".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Guiné Bissau". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Irlanda". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Os portugueses na Noruega". 13 March 2020.
- ^ "Relações Bilaterais Portugal-Itália". Portaldiplomatico.gov.mne.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses em Itália". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Arábia Saudita". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "Relações Bilaterais Portugal-Áustria". Portaldiplomatico.gov.mne.pt.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração: Portugueses na Áustria". Observatorioemigracao.pt.
- ^ "People of the DRC".
- ^ "People of Zambia".
- ^ "People of Jamaica".
- ^ "Embaixada de Portugal na Rússia". Moscovo.embaixadaportugal.mne.pt.
- ^ Faris, Robert N. (2014). Liberating Mission in Mozambique: Faith and Revolution in the Life of Eduardo Mondlane. Wipf and Stock Publishers. ISBN 9781630874841.
- ^ Cavendish, Marshall (2002). Peoples of Europe. Marshall Cavendish. p. 382. ISBN 9780761473787.
- ^ Pop, Ioan-Aurel (1996). Romanians and Hungarians from the 9th to the 14th century. Romanian Cultural Foundation. ISBN 0880334401.
We could say that contemporary Europe is made up of three large groups of peoples, divided on the criteria of their origin and linguistic affiliation. They are the following: the Romanic or neo-Latin peoples (Italians, Spaniards, Portuguese, French, Romanians, etc.), the Germanic peoples (Germans proper, English, Dutch, Danes, Norwegians, Swedes, Icelanders, etc.), and the Slavic peoples (Russians, Ukrainians, Belorussians, Poles, Czechs, Slovaks, Bulgarians, Serbs, Croats, Slovenians, etc.
- ^ Minahan, James (2000). One Europe, Many Nations: A Historical Dictionary of European National Groups. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 533. ISBN 0313309841.
The Portuguese are a Latin nation
- ^ Minahan, James (2000). One Europe, Many Nations: A Historical Dictionary of European National Groups. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 776. ISBN 978-0313309847.
Romance (Latin) nations... Portuguese
- ^ a b says, Soraya Gomes (10 September 2022). "Os 23 povos que deram origem aos portugueses | VortexMag". www.vortexmag.net (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ a b "Batalha de São Mamede". www.leme.pt. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ a b "O Tratado de Zamora". RTP Ensina (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Melvin Eugene Page, Penny M. Sonnenburg, p. 481
- ^ Valdez, Ana T. "(PDF) The First Globalization: The Portuguese and the Age of Discovery". Academia.edu. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ a b "A brief history of globalization". Weforum.org. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Crowley, Roger (15 September 2015). Conquerors: How Portugal seized the Indian Ocean and forged the First Global Empire. Faber & Faber. ISBN 9780571290918.
- ^ Page, Martin (2002). The First Global Village: How Portugal Changed the World. Casa das Letras. ISBN 9789724613130.
- ^ Exenberger, Andreas. "(PDF) The Cradle of Globalisation Venice's and Portugal's Contribution to a World Becoming Global". Academia.edu. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ "Portuguese Communities". Diplomatic Portal. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Celts and the Castro Culture in the Iberian Peninsula – issues of national identity and Proto-Celtic substratum". Ppg.revistas.uema.br. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ https://dc.uwm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1028&context=ekeltoi [bare URL PDF]
- ^ "the Indo-European but clearly non-Celtic language that we today call Lusitanian.(...)": Book Reviews: Alejandro G. Sinner, Javier Velaza (eds.). Palaeohispanic Languages and Epigraphies, Oxford University Press, 2019, Juan Luis García Alonso, University of Salamanca, Spain, Journal of Language Relationship, № 19/3-4, 2021
- ^ "Portugal – History". Britannica. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ Almagro-Gorbea, Martín (14 July 2016). "Vista de "Lancea", palabra lusitana, y la etnogénesis de los "Lancienses"". Complutum. 27 (1). Revistas.ucm.es: 131–168. doi:10.5209/CMPL.53220. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2006). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase. p. 144. ISBN 9781438129181.
- ^ a b c d Bycroft, Clare; et al. (2019). "Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 551. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10..551B. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-08272-w. PMC 6358624. PMID 30710075.
- ^ a b c d Olalde, Iñigo; et al. (2019). "The genomic history of the Iberian Peninsula over the past 8000 years". Science. 363 (6432): 1230–1234. Bibcode:2019Sci...363.1230O. doi:10.1126/science.aav4040. PMC 6436108. PMID 30872528.
- ^ Lenzi, Tié (10 December 2021). "Povo português: conheça as suas origens e características". Nacionalidade Portuguesa Assessoria. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Pöll, Bernhard (26 April 2019), "History of the Portuguese Lexicon", Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Linguistics, doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780199384655.001.0001/acrefore-9780199384655-e-463 (inactive 1 November 2024), ISBN 978-0-19-938465-5, retrieved 18 July 2023
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ "As invasões bárbaras da Península Ibérica". RTP Ensina (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Milhazes, José. Os antepassados caucasianos dos portugueses Archived 2016-01-01 at the Wayback Machine – Rádio e Televisão de Portugal in Portuguese.
- ^ Ivo Xavier Fernándes. Topónimos e gentílicos, Volume 1, 1941, p. 144.
- ^ Oliveira, Ricardo Costa de. "Mitos e Concepções dos Alanos no Ocidente Ibérico". Academia.edu.
- ^ Quiroga, Jorge López (January 2017). "IN TEMPORE SUEBORUM. The time of the Suevi in Gallaecia (411–585 AD). Exhibition Catalogue (English)". Jorge López Quiroga-Artemio M. Martínez Tejera (Coord.): In Tempore Sueborum. The Time of the Sueves in Gallaecia (411–585 Ad). The First Medieval Kingdom of the West, Ourense.
- ^ Nogueiro, I.; Teixeira, J. C.; Amorim, A.; Gusmão, L.; Alvarez, L. (2015). "Portuguese crypto-Jews: the genetic heritage of a complex history". Frontiers in Genetics. 6: 12. doi:10.3389/fgene.2015.00012. PMC 4313780. PMID 25699075.
- ^ Adams, S. M.; Bosch, E.; Balaresque, P. L.; Ballereau, S. J.; Lee, A. C.; Arroyo, E.; López-Parra, A. M.; Aler, M.; Grifo, M. S.; Brion, M.; Carracedo, A.; Lavinha, J.; Martínez-Jarreta, B.; Quintana-Murci, L.; Picornell, A.; Ramon, M.; Skorecki, K.; Behar, D. M.; Calafell, F.; Jobling, M. A. (2008). "The Genetic Legacy of Religious Diversity and Intolerance: Paternal Lineages of Christians, Jews, and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula". American Journal of Human Genetics. 83 (6): 725–736. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.11.007. PMC 2668061. PMID 19061982.
- ^ cite web|url= https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/international-journal-of-middle-east-studies/article/what-does-the-slave-trade-in-the-saqaliba-tell-us-about-early-islamic-slavery/EDDD35D8FD593AB8D576D11550CF62C6%7Ctitle=What does the Slave Trade in the Saqaliba tell us about Early Islamic Slavery|date=1 February 2024
- ^ "The Viking Routes / Les Routes Des Vikings" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- ^ a b "História da Póvoa de Varzim" (in Portuguese). Memória Portuguesa.
- ^ "09" (PDF). Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ a b "Vikings- Warriors from the sea". Portugal.um.dk. Archived from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ "Fenícios e Gregos na Península Ibérica".
- ^ "Porque é que Portugal se chama Portugal?" (PDF).
- ^ "Manuel géographique et statistique de l'Espagne et du Portugal". 25 September 2023.
- ^ "De onde vem o nome Portugal?". 24 June 2021.
- ^ Teresa Ferriera Rodrigues. "HISTÓRIA DA POPULAÇÃO PORTUGUESA : Das longas permanências à conquista da modernidade". Cepese.pt. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ Pericić M, Lauc LB, Klarić IM, Rootsi S, Janićijevic B, Rudan I, et al. (October 2005). "High-resolution phylogenetic analysis of southeastern Europe traces major episodes of paternal gene flow among Slavic populations". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 22 (10): 1964–75. doi:10.1093/molbev/msi185. PMID 15944443.
- ^ Čeština: Distribuce genu R1b napříč Evropou (15 June 2012). "File:R1b-DNA-Distribution – Wikimedia Commons". Commons.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Dupanloup I, Bertorelle G, Chikhi L, Barbujani G (July 2004). "Estimating the impact of prehistoric admixture on the genome of Europeans". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 21 (7): 1361–72. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh135. PMID 15044595. S2CID 17665038.
- ^ Haak, Wolfgang; Lazaridis, Iosif; Patterson, Nick; Rohland, Nadin; Mallick, Swapan; et al. (2 March 2015). "Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe". Nature. 522 (7555). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 207–211. arXiv:1502.02783. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..207H. bioRxiv 10.1101/013433. doi:10.1038/nature14317. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 5048219. PMID 25731166. S2CID 196643946.
- ^ Allentoft, Morten E.; Sikora, Martin; Sjögren, Karl-Göran; Rasmussen, Simon; Rasmussen, Morten; Stenderup, Jesper; Damgaard, Peter B.; Schroeder, Hannes; Ahlström, Torbjörn; Vinner, Lasse; Malaspinas, Anna-Sapfo; Margaryan, Ashot; Higham, Tom; Chivall, David; Lynnerup, Niels; Harvig, Lise; Baron, Justyna; Casa, Philippe Della; Dąbrowski, Paweł; Duffy, Paul R.; Ebel, Alexander V.; Epimakhov, Andrey; Frei, Karin; Furmanek, Mirosław; Gralak, Tomasz; Gromov, Andrey; Gronkiewicz, Stanisław; Grupe, Gisela; Hajdu, Tamás; et al. (2015). "Population genomics of Bronze Age Eurasia". Nature. 522 (7555): 167–172. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..167A. doi:10.1038/nature14507. PMID 26062507. S2CID 4399103.
- ^ Mathieson, Iain; Lazaridis, Iosif; Rohland, Nadin; Mallick, Swapan; Patterson, Nick; Alpaslan Roodenberg, Songul; Harney, Eadaoin; Stewardson, Kristin; Fernandes, Daniel; Novak, Mario; Sirak, Kendra; Gamba, Cristina; Jones, Eppie R.; Llamas, Bastien; Dryomov, Stanislav; Pickrell, Joseph; Arsuaga, Juan Luis; De Castro, Jose Maria Bermudez; Carbonell, Eudald; Gerritsen, Fokke; Khokhlov, Aleksandr; Kuznetsov, Pavel; Lozano, Marina; Meller, Harald; Mochalov, Oleg; Moiseyev, Vayacheslav; Rojo Guerra, Manuel A.; Roodenberg, Jacob; Verges, Josep Maria; et al. (2015). "Eight thousand years of natural selection in Europe". bioRxiv: 016477. doi:10.1101/016477.
- ^ "OS CELTAS". abemdanacao.blogs.sapo.pt. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Cunliffe, Barry (2008). Europe Between the Oceans: Themes and Variations, 9000 BC-AD 1000 (First printed in paperback 2011. ed.). New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 254–258. ISBN 978-0-300-17086-3.
- ^ Bowman, Sheridan; Needham, Stuart (2007). "The Dunaverney and Little Thetford Flesh-Hooks: History, Technology and Their Position within the Later Bronze Age Atlantic Zone Feasting Complex" (PDF). The Antiquaries Journal. 87: 53–108. doi:10.1017/s0003581500000846. S2CID 161084139. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- ^ Mattoso, José (dir.), História de Portugal. Primeiro Volume: Antes de Portugal, Lisboa, Círculo de Leitores, 1992. (in Portuguese)
- ^ Barral-Arca R, Pischedda S, Gómez-Carballa A, Pastoriza A, Mosquera-Miguel A, López-Soto M, et al. (21 July 2016). "Meta-Analysis of Mitochondrial DNA Variation in the Iberian Peninsula". PLOS ONE. 11 (7): e0159735. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1159735B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159735. PMC 4956223. PMID 27441366.
- ^ a b Pimenta, J.; Lopes, A. M.; Carracedo, A.; Arenas, M.; Amorim, A.; Comas, D. (2019). "Spatially explicit analysis reveals complex human genetic gradients in the Iberian Peninsula". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 7825. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.7825P. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-44121-6. PMC 6534591. PMID 31127131.
- ^ Smith, William (1854). "Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography".
- ^ Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2006). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase. ISBN 9781438129181.
- ^ Guest, Edwin (1971). Origines Celticae (A Fragment) and Other Contributions to the History of Britain. Ardent Media. ISBN 9780804612234.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic Culture: A-Celti. Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 9781851094400.
- ^ Ó hÓgáin, Dáithí (2002). The Celts: A History. Cork: The Collins Press. p. 73. ISBN 9780851159232.
- ^ "Lusitani | people". Britannica.com.
- ^ Mallory, James P. (2013). "The Indo-Europeanization of Atlantic Europe". In J. T. Koch; B. Cunliffe (eds.). Celtic From the West 2: Rethinking the Bronze Age and the Arrival of Indo–European in Atlantic Europe. Oxford: Oxbow Books. pp. 17–40. Archived from the original on 26 March 2019. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ^ "New insights into the origin of the Indo-European languages".
- ^ Chao, Eduardo (1849). "Cuadros de la geografia historica de Espana desde los primeros tiempos historicos hasta el dia (Etc.)".
- ^ Corbal, Margarita Vazquez. "The southwestern border between Galicia and Portugal during the 12th and 13th centuries: A space for experimentation and artistic transmission". The Reading Medievalist, 3, "Selected Proceedings from "On the Edge" GCMS Graduate Conference, 2015 – via Academia.
- ^ Ferreira, Marta Leite. "Lisboa não é a capital de Portugal e outros 9 factos que não aprendeu nas aulas de História". Observador.
- ^ "Viriato".
- ^ "Portugal – History". Encyclopedia Britannica. 22 May 2023.
- ^ "Ethnographic Map of Pre-Roman Iberia (circa 200 b". Arkeotavira.com. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ Silva, Luis (30 July 2013). Viriathus: and the Lusitanian Resistance to Rome 155–139 BC. Pen and Sword. ISBN 9781473826892 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Vercingetorix | Gallic chieftain". Encyclopedia Britannica. 8 January 2024.
- ^ "Boudicca | History, Facts, & Death". Encyclopedia Britannica. 12 May 2023.
- ^ MALKIEL, YAKOV (1978). "The Classification of Romance Languages". Romance Philology. 31 (3): 467–500. ISSN 0035-8002. JSTOR 44943149.
- ^ "ASPECTOS DA CONSTITUIÇÃO DO LÉXICO PORTUGUÊS". www.filologia.org.br. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "O Barco Poveiro" – Octávio Lixa Filgueiras, 1ª edição 1966
- ^ Ripoll López, Gisela (1989). "Características generales del poblamiento y la arqueología funeraria visigoda de Hispania". Espacio, Tiempo y Forma, S. I, Prehist. y Arqueol., t. 2. pp. 389–418. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2010. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
En resumen se puede considerar que el pueblo visigodo—sin diferenciar la población civil de la militar— representó de un uno a un dos por ciento sobre la totalidad de la población de Hispania.
- ^ "Les Wisigoths dans le Portugal médiéval : état actuel de la question". L'Europe héritière de l'Espagne wisigothique. Collection de la Casa de Velázquez. Books.openedition.org. 23 January 2014. pp. 326–339. ISBN 9788490960981.
- ^ https://alpha.sib.uc.pt/?q=content/o-património-visigodo-da-l%C3%ADngua-portuguesa [dead link]
- ^ Quiroga, Jorge López (January 2017). "(PDF) IN TEMPORE SUEBORUM. The time of the Suevi in Gallaecia (411–585 AD)". Jorge López Quiroga-Artemio M. Martínez Tejera (Coord.): In Tempore Sueborum. The Time of the Sueves in Gallaecia (411–585 Ad). The First Medieval Kingdom of the West, Ourense. Academia.edu. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ Oliveira, Ricardo Costa de. ""Nós somos Alanos": Documentos, Mitos e Concepções dos Alanos no Ocidente Ibérico".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "The Viking Routes / Les Routes Des Vikings" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- ^ "09" (PDF). Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Jarvis, Judith K.; Levin, Susan L.; Yates, Donald N. (10 May 2018). Book of Jewish and Crypto-Jewish Surnames. Panther's Lodge Publishers. ISBN 9781985856561.
- ^ "Tracing Past Human Male Movements in Northern/Eastern Africa and Western Eurasia". Academic.oup.com. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ Adams SM, Bosch E, Balaresque PL, Ballereau SJ, Lee AC, Arroyo E, et al. (December 2008). "The genetic legacy of religious diversity and intolerance: paternal lineages of Christians, Jews, and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula". American Journal of Human Genetics. 83 (6): 725–36. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.11.007. PMC 2668061. PMID 19061982.
- ^ Numa breve cronologia: 1526 – Alvará de João III, de 13 de Março de 1526, proibiu que os ciganos entrassem no reino, e ordenou que saíssem os que cá estavam; 1538 – Nova lei de 26 de Novembro desse ano, ordenando a sua expulsão; 1592 – Lei de 28 de Agosto agravou as penas contra os ciganos que dentro de 4 meses não saíssem de Portugal; Ordenações Filipinas, proíbindo a entrada no Reino; 1606 – Alvará de 7 de Janeiro exigindo a observância das Ordenações, com a mesma pena agravada com degredo para as galés e com severas cominações para os magistrados remissos; 1614 – Nova carta régia de 3 de Dezembro impedindo a sua entrada no Reino; 1618 – Carta régia de 28 de Março em que o monarca mandava averiguar se no Reino andavam ciganos com «traje e língua diferente dos naturais»; 1654 – D. João IV mandou prender os ciganos que havia no Reino e embarcá-los para Maranhão, Cabo Verde e São Tomé; 1718 – D. João V, em 10 de Dezembro de 1718, determinou a expulsão dos ciganos. Ver Joel Serrão, Dicionário de História de Portugal, ed. de 2006.
- ^ "Auto Da Fé". JewishEncyclopedia.com. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ The Dutch Intersection: The Jews and the Netherlands in Modern History. Brill. 19 June 2008. ISBN 9789047442141.
- ^ "The Sephardic Diaspora After 1492". Myjewishlearning.com. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ http://www.uel.br/seer/index.php/histensino/article/download/11251/10021 [dead link]
- ^ "Jews of Portugal and the Spanish-Portuguese Jewish Diaspora" (PDF). Centrodehistoria-flul.com. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ Ribeiro, Ângelo; Hermano, José (2004), História de Portugal I – A Formação do Território [History of Portugal: The Formation of the Territory] (in Portuguese), QuidNovi, ISBN 989-554-106-6
- ^ Arnaiz-Villena, Antonio (6 December 2012). Prehistoric Iberia: Genetics, Anthropology, and Linguistics. Springer. ISBN 9781461542315.
- ^ Arnaiz-Villena A, Martínez-Laso J, Gómez-Casado E, Díaz-Campos N, Santos P, Martinho A, Breda-Coimbra H (14 May 2014). "Relatedness among Basques, Portuguese, Spaniards, and Algerians studied by HLA allelic frequencies and haplotypes". Immunogenetics. 47 (1): 37–43. doi:10.1007/s002510050324. PMID 9382919. S2CID 11750235.
- ^ a b Galbraith W, Wagner MC, Chao J, Abaza M, Ernst LA, Nederlof MA, et al. (1997). "Imaging cytometry by multiparameter fluorescence". Cytometry. 12 (7): 579–596. doi:10.1002/cyto.990120702. PMID 1782829.
- ^ Gonçalves, Rita; Freitas, Ana; Branco, Marta; Rosa, Alexandra; Fernandes, Ana T.; Zhivotovsky, Lev A.; Underhill, Peter A.; Kivisild, Toomas; Brehm, António (19 April 2005). "Y-chromosome Lineages from Portugal, Madeira and Açores Record Elements of Sephardim and Berber Ancestry". Annals of Human Genetics. 69 (4): 443–454. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00161.x. hdl:10400.13/3018. ISSN 0003-4800. PMID 15996172. S2CID 3229760.
- ^ "Porque querem os galegos ver televisão portuguesa? – Diversidades – Ciberdúvidas da Língua Portuguesa". ciberduvidas.iscte-iul.pt. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Terra, A. Nosa (31 August 2019). ""Decepciona ver galegos difundindo mitos portugueses negadores do galego"". A Nosa Terra (in Galician). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "O "galego" é o "português da Galiza"". Nós Diario (in Galician). 18 July 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Portugal 1929: "Os galegos são nossos irmãos"". Nós Diario (in Galician). 30 August 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "O Galego e o Português São a Mesma Língua?". Artigos com informações, dicas e curiosidades sobre línguas (in Brazilian Portuguese). 6 January 2020. Retrieved 22 May 2023.
- ^ "O Galego e o Português são a mesma língua?".
- ^ "Population on 1 January by age group, sex and country of birth".
- ^ "Statistics Portugal – Web Portal". www.ine.pt. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- ^ a b "Quase 800 mil estrangeiros vivem em Portugal e 30% são brasileiros". 23 June 2023. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023.
- ^ "Idade média: 46,8 anos. População portuguesa é a que mais está a envelhecer na UE". TSF Rádio Notícias (in European Portuguese). 22 February 2023. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ a b "População residente segundo os Censos: total e por grandes grupos etários". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "life expectancy PRT". Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ "Taxa bruta de mortalidade". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Taxa bruta de natalidade". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Taxa bruta de mortalidade e taxa de mortalidade infantil". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Women in the EU are having their first child later". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Portugal – urbanization 2011–2021". Statista. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Statistics Portugal – Web Portal". www.ine.pt. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Union, Publications Office of the European (20 June 2013). "Europeans and their languages : special Eurobarometer. 386, June 2012". op.europa.eu. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Portugal, Rádio e Televisão de (25 October 2022). "Mais de 95% da etnia cigana em Portugal vive abaixo do limiar da pobreza". Mais de 95% da etnia cigana em Portugal vive abaixo do limiar da pobreza (in Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Portuguesa, Observatório da Língua (31 July 2021). "A língua mirandesa é língua oficial em Portugal desde 1999". Observatório da Língua Portuguesa (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ "Língua Mirandesa". Casa de Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro de Lisboa (in European Portuguese). 31 May 2015. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ SAPO. "Têm menos de 20 anos e sentem-se mais livres por falar mirandês". SAPO 24 (in Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Assim se fala o mirandês (in Portuguese), retrieved 11 May 2023
- ^ "Língua Mirandesa". Casa de Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro de Lisboa (in European Portuguese). 31 May 2015. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Unesco.org". Unesco.org. 9 August 2014. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ "Asturiano/Leonés". Azkuefundazioa.eus. Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ^ "Promotora Española de Lingüística". Proel.org. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ^ "Un enclave lingüístico astur-leonés sobrevive en la "raia" portuguesa". Lavozdegalicia.es. 20 March 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ^ "Mirandês é a segunda língua de Portugal".
- ^ Rodrigues, Elisabete (7 February 2020). "O Barranquenho quer ser a 3ª língua oficial de Portugal". Sul Informação (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ "A luta de Vera Ferreira para salvar o minderico". O MIRANTE | A luta de Vera Ferreira para salvar o minderico. (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Vicente, Manuel Fernandes (17 August 2009). "Minderico renasce com apoio da Volkswagen a línguas ameaçadas". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ "Língua Gestual Portuguesa (LGP)". Associação Portuguesa de Surdos (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ "Portal SEF". Sef.pt. Archived from the original on 20 July 2008. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ Kitsoft. "Embaixada da Ucrânia na República Portuguesa – Informação sobre a comunidade ucraniana em Portugal". portugal.mfa.gov.ua (in Portuguese). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Lusa, Agência. "Portugal concedeu mais de 59.000 proteções temporárias desde o início da guerra na Ucrânia". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ cite web=https://inforpress.cv/ucrania-comunidade-ucraniana-passa-a-ser-segunda-maior-residente-em-portugal/ Archived 27 June 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Refugiados y migrantes de Venezuela | R4V". www.r4v.info. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "CIGANOS, UM PASSADO, UM PRESENTE E QUE FUTURO?". Errc.org. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ "Mais de 95% da etnia cigana em Portugal vive abaixo do limiar da pobreza". 25 October 2022.
- ^ Reis Oliveira, Catarina; Gomes, Natália (July 2019). Estatísticas do Bolso da Imigração. Observatório das Migrações, ACM, I.P. ISBN 9789896851019.
- ^ "Imigração para Portugal já cresceu 18% em 2019 (e ainda vai aumentar)". Jornal Expresso.
- ^ "A Comunidade Islâmica de Lisboa faz 50 anos. E "o Islão está na alma de Portugal"". Imigrantes.no.sapo.pt. Archived from the original on 26 September 2014. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ ""A comunidade muçulmana em Portugal dá-nos uma grande tranquilidade na prevenção do terrorismo"". 20 September 2022.
- ^ "Por que judeus estão voltando a Portugal séculos após antepassados serem expulsos e massacrados". BBC News Brasil.
- ^ "How many Jews live in Portugal? | JPR". www.jpr.org.uk. 5 January 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Exodus? The Jewish Community in This European City Is Thriving". Haaretz. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "New dawn: Portugal Jewish community springs to life".
- ^ "SEFSTAT – Portal de Estatística". sefstat.sef.pt. Retrieved 25 May 2023.
- ^ Registo Civil, Instituto dos Registos e Notariado, Ministério da Justiça. "Composição do nome" [Composition of the name]. IRN.Justica.gov.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 3 August 2022.
«O nome completo deve compor-se, no máximo, de seis vocábulos gramaticais, simples ou compostos, dos quais só dois podem corresponder ao nome próprio e quatro a apelidos.»
- ^ "FAQs e Dicas – SPIE". Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2013. (a fonte utilizada enuncia "100 apelidos", mas a listagem traz apenas 96).
- ^ "Os 100 Apelidos mais frequentes da População Portuguesa" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ^ "Apellidos clasificaciones". Mapa De Sobrenomes (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 24 February 2023.
- ^ "descendentes ou membros da comunidade". vcportugalpoa (in Portuguese). Retrieved 15 May 2023.
- ^ "The Portuguese Diaspora – PILOT GUIDES". 25 January 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2023.
- ^ "Portugal ǀ Portuguese ǀ Iberian". DNA Consultants. Retrieved 15 May 2023.
- ^ "The Bayingyi People of Burma". Joaoroqueliteraryjournal.com. 6 February 2018.
- ^ "Portugal – Emigration". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ Malheiros, Jorge (1 December 2002). "Portugal Seeks Balance of Emigration, Immigration". Migrationpolicy.org. Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ "Estatísticas gerais: imigrantes e descendentes" [General statistics: immigrants and descendants] (in Spanish). State Government of São Paulo. Archived from the original on 25 April 2006. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ^ Direcção Geral dos Assuntos Consulares e Comunidades Portuguesas do Ministério dos Negócios Estrangeiros (1999), Dados Estatísticos sobre as Comunidades Portuguesas, IC/CP – DGACCP/DAX/DID – Maio 1999.
- ^ "Migration – Portugal – average, annual". Nationsencyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "How Spain and Portugal Expelled Their Jews". My Jewish Learning. Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ "Cristãos-Novos no Brasil Colônia" [New-Christians in colonial Brazil] (in Portuguese). IBGE. Archived from the original on 6 March 2001. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- ^ "Cristãos-novos". Mundo Educação (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ "Crypto Jews: What is the history of secret Jews? – explainer". The Jerusalem Post. 23 August 2022. Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ Ayoun, Richard (2002). "L'établissement des crypto-juifs portugais à Nantes au XVIe siècle". Actes des congrès nationaux des sociétés historiques et scientifiques. 124 (11): 303–320.
- ^ "HISTÓRIA DA POPULAÇÃO PORTUGUESA : Das longas permanências à conquista da modernidade".
- ^ Stolk, Marijn (31 December 2018). "Exploring Immigrant Identities: The Link between Portuguese Ceramics and Sephardic Immigrants in 17th Century Amsterdam: Marijn Stolk". Ex Novo: Journal of Archaeology. 3: 101–120. doi:10.32028/exnovo.v3i0.383. ISSN 2531-8810. S2CID 166900120.
- ^ Tomashevich, George Vid (1982). "BALKAN JEWS AND THEIR NEIGHBORS BEFORE, DURING AND SINCE THE HOLOCAUST: A Study in Ethno-Religious (and Ideological) Relations". Humboldt Journal of Social Relations. 10 (1): 339–363. ISSN 0160-4341. JSTOR 23261871.
- ^ "Italy". Sephardic Genealogy. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Sephardi Jews in the Ottoman Empire – Portuguese Citizenship –". Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "The Sephardic Exodus to the Ottoman Empire". My Jewish Learning. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "O português dos judeus na Europa no começo do séc. XX – Ciberdúvidas da Língua Portuguesa". ciberduvidas.iscte-iul.pt. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Papiamentu | language | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "the world". Ethnologue (Free All). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Jewish slaveowners celebrate Passover in 17th-century Suriname".
- ^ "The History of Sranan, A Language of Suriname". linguistics.byu.edu. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Abrunhosa, Maria Eugénia (1 December 2020). ""Portugueses no Holocausto": o "descarinho" que acabou em Auschwitz". Sete Margens (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Portugueses no holocausto – A Esfera dos Livros" (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Salazar negou auxílio a judeus na Grécia e na Holanda". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 29 October 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Salazar foi cúmplice "involuntário" do Holocausto". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 29 October 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Salazar evitou o auxílio a judeus portugueses na Grécia e na Holanda". TVI Notícias (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Artes – Prémio distingue pesquisa sobre judeus de origem portuguesa em França salvos do Holocausto". RFI (in Portuguese). 7 February 2023. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Yad Vashem : Aristides De Sousa Mendes".
- ^ "Quem foi o diplomata que ficou conhecido como 'Schindler de Portugal' por salvar milhares de judeus do Holocausto". G1 (in Brazilian Portuguese). 19 October 2021. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese Law of Return". Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese Law: Sephardic descendants eligible to obtain Portuguese Citizenship – Sponsored Content | The Times of Israel". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Getting The Portuguese Citizenship For The Sephardic Jews". Abitbol Associes. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Nationality: Acquisition by Descendants of Sephardic Jews". Embassy of Portugal to the United States of America. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Renascença. "Renascença – A par com o mundo". Rádio Renascença (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Machado, Alexandra. "Mais de 30 mil descendentes de sefarditas receberam cidadania portuguesa desde 2015". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Lusa, Agência. "Descendentes sefarditas a viver no estrangeiro foram quem mais obteve a cidadania portuguesa". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Sefarditas de mais de 60 países pediram nacionalidade portuguesa". TSF Rádio Notícias (in European Portuguese). 16 February 2022. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Pomerantz, Leandro Da Mota Damasceno, Ian (14 March 2023). "O que aconteceu à "reparação histórica mais progressista" da Europa?". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jones, Sam; Silva, Beatriz Ramalho da (16 March 2022). "Portugal to change law under which Roman Abramovich gained citizenship". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Les secrets de la ruée sur les passeports portugais". Le Monde.fr (in French). 27 February 2023. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Descendentes de judeus sefarditas correm por nacionalidade em Portugal antes de nova regra". Folha de S.Paulo (in Brazilian Portuguese). 6 May 2022. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Santos, Eurico (6 April 2023). "Comunicado do Conselho de Ministros de 6 de abril de 2023". www.homepagejuridica.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Camille Pissarro". My Jewish Learning. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ "Louisa Benson Craig Dies Aged 69". www2.irrawaddy.com. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ Arom, Eitan (3 January 2018). "Charmaine Craig Ponders Her Mixed Jewish and Karen Heritage in 'Miss Burma'". Jewish Journal. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ^ U.S. Department of State, "A GUIDE TO THE UNITED STATES' HISTORY OF RECOGNITION, DIPLOMATIC, AND CONSULAR RELATIONS, BY COUNTRY, SINCE 1776: PORTUGAL", [1]
- ^ Rodrigues, Hugo (12 June 2015). "Misteriosa "Pedra de Dighton" terá uma réplica em Tavira". Sul Informação (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Couto, António (2 April 2023). "História e Memória: A Pedra de Dighton (1511)". História e Memória. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "A PEDRA DE DIGHTON! – AEA" (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Monumentos". www.monumentos.gov.pt. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Santos, Robert L. (1995). "Azorean Immigration Into the United States". Archived from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- ^ Klemin, Jeremy (10 April 2023). "How Should Portuguese Americans Be Classified?". The Atlantic. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "| Portuguese Americans are organized and well connectedPortuguese American Journal". Portuguese American Journal. 13 April 2011. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "The Portuguese in the United States". www.loc.gov. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ davide. "Portuguese-Americans in the U.S. Armed Forces". Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Chronology, 1958–Present". Portuguese Immigrants in the United States. Library of Congress Hispanic Division. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ^ "Text of H.Res. 1438 (110th): Commemorating the 50th anniversary of the Azorean Refugee Act of 1958 and celebrating ... (Passed the House version) – GovTrack.us". GovTrack.us. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- ^ "Azorean-Americans: The Azorean Refugee Act". Portugal.com. 22 September 2022. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Ponta-Garça, Nelson, director. Portuguese in New England. 2016.
- ^ Martin, Andrea. "Carpenter Street Underpass" (PDF). Springfield Railroads Improvement Project. US Department of Transportation Federal Railroad Administration and the Illinois Historic Preservation Agency. Retrieved 23 May 2018.
- ^ Baganha, Maria Ioannis Benis (1991). "The Social Mobility of Portuguese Immigrants in the United States at the Turn of the Nineteenth Century". The International Migration Review. 25 (2): 277–302. doi:10.1177/019791839102500202. JSTOR 2546289. S2CID 147321899 – via JSTOR.
- ^ "Ethnic Origin, Single and Multiple Ethnic Origin Responses and Sex for the Population of Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2006 Census – 20% Sample Data". Retrieved 10 November 2010.
- ^ Lusa, Agência. "Principal rua do 'Little Portugal' em Toronto muda de nome e reescreve a história". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Resident, Portugal (18 October 2022). "A little piece of Portugal in Canada". Portugal Resident. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Renascença (7 July 2017). "Os passos tímidos da língua portuguesa no Canadá – Renascença". Rádio Renascença (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ "Português no Canadá – Ciberdúvidas da Língua Portuguesa". ciberduvidas.iscte-iul.pt. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ "Aprendizagem e ensino de português". Consulado Geral de Portugal em Montreal (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ Janarra, Rui (18 August 2022). "Línguas no Canadá: 118.730 cidadãos falam português em casa, segundo Statcan". Correio da Manhã Canadá (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ "Aliança de associações portuguesas no Canadá luta para manter as tradições – Mundo Português" (in European Portuguese). 20 May 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ Brazão, Isabel. "Fama do fado leva estrangeiros a aprender português no Canadá". ccmm.madeira.gov.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ SAPO. "Cristiano Ronaldo é estímulo para jovens aprenderem português no Canadá". SAPO Lifestyle (in Portuguese). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ Hamilton, William B. (1978): The Macmillan book of Canadian place names, Macmillan of Canada, Toronto, p. 105.
- ^ "Portuguese Exploration along the Northeast Coast of North America". www.loc.gov. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Jamaica National Heritage Trust – The People Who Came". www.jnht.com. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Madeiran Portuguese Migration to Guyana, St. Vincent, Antigua and Trinidad: A Comparative Overview".
- ^ "What Languages Are Spoken in Antigua and Barbuda?". WorldAtlas. 16 September 2019. Retrieved 13 May 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese emigration from Madeira to British Guiana". Guyana.org. 7 May 2000. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ a b "Português Língua de Herança: Um estudo da tentativa da manutenção de uma língua praticamente extinta, em Trinidad e Tobago".
- ^ Pidduck, Angela (14 June 1999). "Small TT / Portuguese Community Continues to Celebrate Heritage". nalis.gov.tt. Archived from the original on 25 February 2002. Retrieved 7 September 2008.
- ^ Rampersad, Joan (7 December 2019). "Portuguese celebrate 185 years in TT – Trinidad and Tobago Newsday". newsday.co.tt. Retrieved 13 May 2023.
- ^ a b "The Portuguese presence". Guyana Chronicle. 5 May 2019. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Kempadoo, Kamala (21 September 2017). "'Bound Coolies' and Other Indentured Workers in the Caribbean: Implications for debates about human trafficking and modern slavery". Anti-Trafficking Review (9): 48–63. doi:10.14197/atr.20121794. ISSN 2287-0113.
- ^ "The Arrival of the Portuguese in British Guiana". Guyana Chronicle. 2 January 2018. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Ogle Airport Renamed Eugene F. Correia International". NevisPages.com. 11 May 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Project, Joshua. "Portuguese in Jamaica". joshuaproject.net. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Mirvis, Stanley (2020). The Jews of Eighteenth-Century Jamaica: A Testamentary History of a Diaspora in Transition. Yale University Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctv10sm932. ISBN 978-0-300-23881-5. JSTOR j.ctv10sm932. S2CID 219044870.
- ^ "Portuguese In Jamaica | Why and When Did They Arrive?". My-Island-Jamaica.com. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ Community (13 October 2020). "Jews in Jamaica". The Jewish Museum London. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "PORTUGALITY in Jamaica". portugality.yolasite.com. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 2012 Census" (PDF).
- ^ "The Portuguese of the West Indies". Freepages.genealogy.rootsweb.ancestry.com. 31 July 2001. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ "Grenada – Population and Housing Census 2001". catalog.ihsn.org. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "UNECLAC-CELADE::Redatam Webserver | Statistical Process and Dissemination Tool". redatam.org. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Saint Kitts and Nevis" (PDF). 5 February 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2018. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Cayman Islands 2010 census" (PDF).
- ^ a b "Quase metade dos habitantes de uma ilha paradisíaca são portugueses". 9 February 2013.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Quatro portugueses retirados de ilha em Cuba devido ao furacão". www.jn.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "Bermuda". Solarnavigator.net. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ a b Lusa, Agência. "Emigrantes nas Bermudas deixam de visitar Portugal por não poderem conduzir no país". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ Portuguese community 'still not accepted', The Royal Gazette, 27 November 2015.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Rodrigues, Andreia (9 June 2021). "Os portugueses no México, destinos traçados com armas e com gosto de tequila". El Trapezio (in European Spanish). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "History". Portu Ricans – Portuguese Puerto Ricans. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ a b c "Maior comunidade portuguesa da América Latina esperançada numa nova Venezuela". Jn.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Colombia – Inmigración 2020 | Datosmacro.com". datosmacro.expansion.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- ^ SAPO. "Colômbia atrai portugueses interessados em negócios e é uma opção à Venezuela". SAPO 24 (in Portuguese). Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Inmigración portuguesa al Perú – Espejo del Perú
- ^ a b c "A emigração 'invisível' dos portugueses na região platina".
- ^ a b "MINHOTOS NA ARGENTINA CELEBRAM PORTUGAL". bloguedominho.blogs.sapo.pt. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ a b Ojeda, Luis Thayer (1989). "origenes de chile:elementos etnicos, apellidos, familas".
- ^ "Portugueses no Uruguai. São Carlos de Maldonado. 1764". www.esteditora.com.br. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ "A Fundação da Colônia do Sacramento".
- ^ Our last Lusitanians Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine (in Spanish)
- ^ Carreiras, Helena (4 January 2024). "Portugueses no Uruguai".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração".
- ^ "Perguntas frequentes". Consulado Geral de Portugal em Montreal (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ http://www.monografias.com/trabajos16/portugueses-en-argentina/portugueses-en-argentina.shtml Inmigración a la Argentina. Portugueses
- ^ Olavarria Portuguese society participated in "Buenos Aires celebrates Portugal" "Infoeme.com – Diario on line de Olavarria". Archived from the original on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ^ Portugal – Emigration, Eric Solsten, ed. Portugal: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1993.
- ^ "O Retorno" (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Argélia". Portaldascomunidades.mne.pt.
- ^ "Portugueses em Botsuana – Expats portugueses em Botsuana". Internations.org.
- ^ Dismantling the Portuguese Empire, Time (7 July 1975)
- ^ "Portugueses são mais parecidos com os argelinos do que costumamos pensar". TSF Rádio Notícias. 10 March 2015.
- ^ "Argélia quer formação profissional portuguesa". Dinheirovivo.pt. 29 November 2018. Archived from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 6 December 2019.
- ^ "Mia Couto ao Expresso: "Somos todos biologicamente mestiços. Os vírus moram dentro de nós"". Jornal Expresso (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Angola: "Houve independência mas não descolonização das mentes"". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). 11 January 2015. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Filho, João Lopes (9 December 2011). "Mestiçagem, emigração e mudança em Cabo Verde". Revista África (in Portuguese) (29–30): 129–140. doi:10.11606/issn.2526-303X.v0i29-30p129-140. ISSN 2526-303X. S2CID 249832231.
- ^ "Quando todo mundo virou mestiço". Expresso das Ilhas (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Andorra statistics".
- ^ "en AndorraInfo.com". AndorraInfo (in European Spanish). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Andorra languages - 1".
- ^ "Andorra languages - 2" (PDF).
- ^ "Eurobarometer". europa.eu. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Portugueses falam cada vez mais (e melhor) línguas estrangeiras". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ ""Tive colegas de escola cujos pais eram portugueses. Mas nunca os vi como uma comunidade. Eram amigos"". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Lusa, PÚBLICO (25 September 2019). "Português é uma das línguas estrangeiras ensinadas em França, Espanha e Roménia". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ a b "A Lisbonne, une visite d'Elisabeth Borne dédiée à la culture et aux dossiers énergétiques". LEFIGARO (in French). 29 October 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "L'immigration portugaise en France au 20ème siècle | Musée de l'histoire de l'immigration". www.histoire-immigration.fr (in French). Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ "História da Emigração em França destaca envio de trabalhadores e xenofobia". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ "france 2 actualités & société". info.france2.fr. Retrieved 28 August 2017.[permanent dead link]
- ^ étrangères, Ministère de l'Europe et des Affaires. "Présentation du Portugal". France Diplomatie : : Ministère de l'Europe et des Affaires étrangères.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ^ Infopédia. "Emigração massiva dos anos 60 – Infopédia". infopedia.pt – Porto Editora (in Portuguese). Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ "RELATÓRIO DA EMIGRAÇÃO" (PDF).
- ^ "Francais et immigres a l'epreuve de la crise (1973-1995)".
- ^ Malik, Matheo (17 October 2023). "La guerre et le pétrole : mythe, réalité et héritage du choc de 1973". Le Grand Continent (in French). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ Zancarini-Fournel, Michelle (2000). "La construction d'un "problème national" : l'immigration. 1973, un tournant ?". Cahiers de la Méditerranée. 61 (1): 147–157. doi:10.3406/camed.2000.1297.
- ^ "1973-1974, du pétrole et des idées : épisode • 3/4 du podcast Après la crise, demain est-il un autre jour ?". France Culture (in French). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ a b "Andorra". Portal Diplomático (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ a b "Lugares no fim do mundo".
- ^ a b "Há portugueses que admitem "renunciar à nacionalidade" devido à burocracia nos consulados belgas". Jornal Expresso (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ statistique, Office fédéral de la (25 January 2021). "Pratiques linguistiques en Suisse – Premiers résultats de l'Enquête sur la langue, la religion et la culture 2019 | Publication". Office fédéral de la statistique (in French). Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ INE. "Indicador". tabulador.ine.pt. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Cerca de 60 mil portugueses emigraram em 2022, Suíça volta a ser principal destino". Expresso (in Portuguese). 29 January 2024. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Angekommen – Armando Rodrigues de Sa". iberer.angekommen.com. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Almeida, José Carlos Pina; Corkill, David (2010). "Portuguese Migrant Workers in the UK: A Case Study of Thetford, Norfolk". Portuguese Studies. 26 (1): 27–40. doi:10.1353/port.2010.0019. ISSN 0267-5315. JSTOR 41105329. S2CID 245842608.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ a b "UK-Portuguese Newspaper Launched in Thetford Norfolk".
- ^ "Population by country of birth and nationality (Discontinued after June 2021)".
- ^ a b "Observatório da Emigração". NewswireToday. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- ^ "Brasil: 500 anos de povoamento" [Brazil: 500 years of settlement] (in Portuguese). IBGE. Archived from the original on 23 September 2009. Retrieved 29 December 2011.
- ^ a b Pinto Venâncio, Renato (2000). "Presença portuguesa: de colonizadores a imigrantes" [Portuguese presence: from settlers to immigrants] (in Portuguese). IBGE. Archived from the original on 24 November 2002.
- ^ History of Immigration to the United States#Population in 1790
- ^ a b "Desmundo de Alain Fresnot, o Brasil no século XVI". ensinarhistoria. 27 February 2015. Archived from the original on 8 October 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ "Desmundo by Ana Miranda (1996)". companhiadasletras.com.br. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ "Desmundo by Ana Miranda". companhiadasletras.com.br. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ Sarkissian (2000), p. 22.
- ^ a b c Ribeiro, Darcy. O Povo Brasileiro, Companhia de Bolso, fourth reprint, 2008 (2008)
- ^ "População indígena no Brasil".
- ^ "Navios portugueses e brasileiros fizeram mais de 9 mil viagens com africanos escravizados". BBC News Brasil (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 14 May 2023.
- ^ "A Integração social e económica dos emigrantes portugueses no Brasil" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 December 2016. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ http://ich.unito.com.br/materia/resource/download/41917 [permanent dead link]
- ^ Do outro lado do Atlântico: um século de imigração italiana no Brasil. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ "A integração social e económica dos imigrantes portugueses no Brasil nos finais do século xix e no século xx" (PDF). Analisesocial.ics.ul.pt. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ Reis, João José (2000). "Evolução da população brasileira segundo a cor" [Evolution of the Brazilian population according to colour] (in Portuguese). Rio de Janeiro: IBGE. Archived from the original on 5 March 2001. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- ^ Carvalho, R., Pelos mesmos direitos do imigrante, 2003 Archived 12 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Observatório da Imprensa from the State University of Campinas (Brazil).
- ^ Parra FC, Amado RC, Lambertucci JR, Rocha J, Antunes CM, Pena SD (January 2003). "Color and genomic ancestry in Brazilians". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (1): 177–82. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100..177P. doi:10.1073/pnas.0126614100. PMC 140919. PMID 12509516.
- ^ Pena SD, Di Pietro G, Fuchshuber-Moraes M, Genro JP, Hutz MH, Gomes Kehdy F, et al. (February 2011). "The genomic ancestry of individuals from different geographical regions of Brazil is more uniform than expected". PLOS ONE. 6 (2): e17063. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...617063P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017063. PMC 3040205. PMID 21359226.
- ^ Saloum de Neves Manta F, Pereira R, Vianna R, Rodolfo Beuttenmüller de Araújo A, Leite Góes Gitaí D, Aparecida da Silva D, et al. (2013). "Revisiting the genetic ancestry of Brazilians using autosomal AIM-Indels". PLOS ONE. 8 (9): e75145. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...875145S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075145. PMC 3779230. PMID 24073242.
- ^ Lima-Costa MF, Rodrigues LC, Barreto ML, Gouveia M, Horta BL, Mambrini J, et al. (April 2015). "Genomic ancestry and ethnoracial self-classification based on 5,871 community-dwelling Brazilians (The Epigen Initiative)". Scientific Reports. 5 (1): 9812. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E9812.. doi:10.1038/srep09812. PMC 5386196. PMID 25913126.
- ^ NOVAimagem.co.pt / Portugal em LInha (17 February 2006). "Cinco milhões de netos de emigrantes podem tornar-se portugueses". Noticiaslusofonas.com. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Cultural diversity: Census, 2021 | Australian Bureau of Statistics". www.abs.gov.au. 12 January 2022. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese Festival at Petersham, Sydney – YouTube"
- ^ "List of numerous Portuguese Social Clubs and institutions based in Australia (Portuguese) Archived 24 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine"
- ^ Cahen, Michel (1 January 2012), "Anticolonialism & Nationalism: Deconstructing Synonymy, Investigating Historical Processes. Notes on the Heterogeneity of Former African Colonial Portuguese Areas", Sure Road? Nationalisms in Angola, Guinea-Bissau and Mozambique, BRILL, pp. 1–28, doi:10.1163/9789004226012_003, ISBN 9789004222618, retrieved 17 May 2023
- ^ "Portugal country brief - Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". 14 October 2010. Archived from the original on 14 October 2010. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ a b Brazão, Isabel. "Portugueses na Austrália e Nova Zelândia mais próximos de Portugal". ccmm.madeira.gov.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese in New Zealand".
- ^ "New Caledonia people groups, languages and religions | Joshua Project". joshuaproject.net. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Nova Deli por quem lá vive: Jorge Roza de Oliveira". Almadeviajante.com. 10 April 2014.
- ^ Reis, Bárbara (7 January 2017). "Portugal quer redescobrir a Índia. Outra vez". Publico.pt.
- ^ "Keturunan Portugis Bermata Biru dan Rambut Pirang Masih Ditemukan di Lamno Raya". Serambinews.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Mengagumi Kecantikan Muslim Mata Biru Keturunan Portugis yang Hidup di Lamno". StatusAceh. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Anjani, Anatasia. "Seperti Orang Eropa, Ini 3 Suku di Indonesia yang Bermata Biru". detikedu (in Indonesian). Jakarta: detikcom. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Kampung Tugu, Jejak Portugis di Utara Jakarta (in Indonesian), 6 March 2023, retrieved 17 May 2023
- ^ Aditya, Nicholas Ryan (3 November 2019). Agmasari, Silvita (ed.). "Menelusuri Kampung Tugu, Jejak Portugis di Utara Jakarta Halaman all". KOMPAS.com (in Indonesian). Jakarta: Kompas Cyber Media. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Lusodescendentes em Java". 29 June 2019.
- ^ "PUSAT DATA KEMENTERIAN AGAMA RI". 3 September 2020. Archived from the original on 3 September 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Similarities Between Indonesian and Portuguese, 29 June 2019, retrieved 17 May 2023
- ^ "INDONESIAN LOANWORDS FROM PORTUGUESE". Learn Indonesian. 23 June 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "The borrowed words of Bahasa Indonesia: Exploring the roots of a deeply dynamic language". SBS Language. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ a b Thu, Mratt Kyaw (6 December 2017). "The 400-year history of Portuguese Catholics in Sagaing". Frontier Myanmar. Retrieved 8 May 2019.
- ^ a b "The Bayingyi People of Burma". Joao-Roque Literary Journal est. 2017. 6 February 2018. Retrieved 11 May 2019.
- ^ a b c Combustões (19 July 2009). "Portuguese descendants in Thailand". 500anosportugaltailansda.blogspot.com. Retrieved 8 May 2019.
- ^ "Bangkok enclave celebrates its Portuguese past". Asia.nikkei.com.
- ^ a b "ความสัมพันธ์ไทย-โปรตุเกส" (PDF).
- ^ Low, Spencer (26 March 2023). "How Portuguese influence in Sri Lanka outlasted that of the Dutch". Portuguese in Asia. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "THE RISE AND FALL OF THE PORTUGUESE LANGUAGE IN SRI LANKA". www.icm.gov.mo. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Jayasuriya, Shihan de Silva (2000). "The Portuguese Cultural Imprint on Sri Lanka". Lusotopie. 7 (1): 253–259.
- ^ Jayasuriya, Shihan de Silva (30 November 2005). "The Portuguese Identity of the Afro-Sri Lankans". Lusotopie. Recherches politiques internationales sur les espaces issus de l'histoire et de la colonisation portugaises. 12 (XII(1–2)): 21–32. doi:10.1163/176830805774719755. ISSN 1257-0273.
- ^ HETTIARATCHI, D. E. (1965). "Influence of Portuguese on the Sinhalese Language". The Journal of the Ceylon Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain & Ireland. 9 (2): 229–238. ISSN 0304-2235. JSTOR 45377565.
- ^ Digest, Ceylon (22 February 2020). "The Portuguese Burghers of Sri Lanka". Ceylon Digest. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Travel, Diamond Tours and. "5 Marcos da Herança Portuguesa no Sri Lanka que permanecem até hoje". www.diamondtoursandtravel.com (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ DIA, BOM (8 May 2023). "Salvar o crioulo português do Sri Lanka é urgente". BOM DIA (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ a b "Celebrating Karachi's Goan connection | The Express Tribune". tribune.com.pk. 16 April 2022. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ a b Correa, Noel (12 June 2011). "Pakistan's Portuguese wonder: Magic fingers". The Express Tribune. Retrieved 10 August 2015.
- ^ "Flashback: From Goa with love". Dawn. 16 September 2012. Retrieved 10 August 2015.
- ^ Alam, Dhrubo (22 January 2018). "The Portuguese in Dhaka". The Daily Star. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Viaggio Apostolico di Sua Santità Francesco in Myanmar e Bangladesh (26 novembre-2 dicembre 2017) – Statistiche". press.vatican.va. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Renascença (30 November 2017). "Rozario, Costa e Gomes esperam Papa no Bangladesh – Renascença". Rádio Renascença (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Bangladesh. O que é "Joy Bangla"?". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 24 August 2022. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Bangladesh". Camões, I.P. (in European Portuguese). 4 May 2017. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ Renascença (31 January 2018). "Bangladesh. A história de fé de um povo que usa com orgulho o apelido português – Renascença". Rádio Renascença (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Um treinador português no Bangladesh: "Ganhe ou não, preciso de um desafio novo"". www.ojogo.pt (in European Portuguese). 30 October 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Luso-Indian | Indian people | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Embaixada de Portugal em Tóquio | Portal dedicado à divulgação das atividades da Embaixada de Portugal em Tóquio. Disponível informação relativa a relações bilaterais entre Portugal e Japão, Agência para o Investimento e Comércio Externo de Portugal, Secção Consular e Secção Cultural, bem como todos os contactos úteis, localização e horários de funcionamento". Embaixadadeportugal.jp. Archived from the original on 29 May 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- ^ a b "在留外国人統計(旧登録外国人統計) 在留外国人統計 月次 2020年12月 | ファイル | 統計データを探す". 政府統計の総合窓口 (in Japanese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Yuanyuan, Cui (2017). Portugueses na China: um exame da situação atual (masterThesis thesis).
- ^ "Immigration to Taiwan".
- ^ a b "Comunidades Portuguesas no Mundo". Archived from the original on 7 October 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "2008 Community Survey". Factfinder.census.gov. Archived from the original on 11 February 2020. Retrieved 18 September 2012.
- ^ ""Nós unimos, não dividimos, nós criamos a paz, não a guerra"". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 11 June 2018. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "TVI Internacional disponível para 1 milhão e 400 mil portugueses nos EUA". Jornal SOL (in Portuguese). 15 July 2013. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ Statistics Canada (8 May 2013). "2011 National Household Survey: Data tables". Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ Renascença (7 July 2017). "Os passos tímidos da língua portuguesa no Canadá – Renascença". Rádio Renascença (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Esquema relacionado com burla na imigração está a preocupar portugueses no Canadá". SIC Notícias (in Portuguese). 10 January 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ ""Portugueses no Canadá são embaixadores de Portugal"". www.theportugalnews.com (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Escola de português nas Bermudas procura acreditação junto do instituto Camões". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 19 November 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Associação dos Emigrantes Açorianos foi às Bermudas para registar História de 175 anos de presença portuguesa". Diario dos Açores (in European Portuguese). Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Governo dos Açores considera urgente reconhecimento em Portugal das cartas de condução emitidas nas Bermudas". Rádio Lumena (in European Portuguese). 12 August 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ SAPO. "Marco tem "dinheiro fresco" na Bermuda, mas sente falta da gastronomia açoriana". SAPO 24 (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Azoreans in Bermuda – AEA". Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ aportugueseaffair (30 May 2017). "Portuguese Heritage in Bermuda • A Portuguese Affair". A Portuguese Affair. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "People of Jamaica".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ a b "Historial da Emigração da R.A.M." ccmm.madeira.gov.pt. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "PR/México: Marcelo salienta crescimento das relações económicas e da comunidade portuguesa". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 14 July 2017. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "2011 Population and Housing Census Demographic Report Trinidad and Tobago".
- ^ "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines census" (PDF).
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Cayman Islands 2010 Census" (PDF).
- ^ "Antigua and Barbuda 2011 Census" (PDF).
- ^ NOVAimagem.co.pt / Portugal em LInha (17 February 2006). "Notícias do Brasil | Noticias do Brasil, Portugal e países de língua portuguesa e comunidades portuguesas". Noticiaslusofonas.com. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Froilán Ramos Rodríguez: Un estudio sobre la inmigración portuguesa a Venezuela".
- ^ "Inmigración portuguesa al Perú".
- ^ "Buenos Aires celebra Portugal (fotogaleria)". Jornal Expresso (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "10 de Junho: Instituições na Argentina celebram em conjunto pela 1.ª vez". Notícias ao Minuto (in Portuguese). 10 June 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Quando os portugueses na Argentina falam de Portugal é à sua aldeia que se referem". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese : Small in numbers but big in business". 5 May 2021.
- ^ SAPO. "Colômbia atrai portugueses interessados em negócios e é uma opção à Venezuela". SAPO 24 (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Embaixada de Portugal na Colômbia". Embaixada de Portugal na Colômbia (in European Portuguese). 14 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Country-of-birth database". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Archived from the original (XLS) on 11 May 2005. Retrieved 30 July 2009.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". Sem.admin.ch.
- ^ Lusa, Agência. "Brexit: Portugueses no Reino Unido desesperam para renovar documentos". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Portugueses no Reino Unido" (PDF).
- ^ "Isabel II: Portugueses no Reino Unido mais preocupados com economia do que com realeza". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 13 September 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração" (in Portuguese).
- ^ "Estadística de extranjeros residentes en España".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração" (in French). Statec. Retrieved 1 July 2007.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". Observatorioemigracao.pt. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese in Jersey" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 April 2022. Retrieved 19 May 2022.
- ^ Moura, Sara. "Clubes desportivos dão vida e visibilidade à comunidade portuguesa em Jersey". ccmm.madeira.gov.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ ""Nossa moeda é a fé": Como uma igreja impediu que um templo virasse um restaurante". Notícias Gospel. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Fluxo começou na década de 50". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). 28 November 2005. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ Pisco, Paulo (13 March 2020). "Os portugueses na Noruega". BOM DIA (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Itália". Portal Diplomático (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Áustria". Portal Diplomático (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Dinamarca". Portal Diplomático (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ Archer, Edward G. (2006). Gibraltar, Identity and Empire. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-34796-9.
- ^ "Convidado - Rede de portugueses na Polónia já conseguiu enviar 30 ucranianos para Portugal". RFI (in Portuguese). 14 March 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Portuguese in the UK".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Portugueses no Liechtenstein".
- ^ "Liechtenstein". Portal Diplomático (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ Macao Country Study Guide Volume 1 Strategic Information and Developments. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "National Geographic Portugal". nationalgeographic.pt. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Mianmar. A terra em que houve reis portugueses". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 3 December 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ Castro, Joaquim Magalhães de (12 March 2011). "A ilha dos portugueses". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Casas incendiadas, terror e morte em Myanmar: Luso-descendentes católicos Bayingyi no alvo dos militares". SBS Language (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ (in Portuguese)Sidney Arnold Pakeman, "Ceylon", Praeger, 1964
- ^ (in Portuguese)
- ^ "The Malaccan Portuguese Creole: Papia Kristang". HKU Malaysia 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Uma história da língua" (PDF).
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Hong Kong – "Club Lusitano é a casa de todos os portugueses"". 2021.
- ^ "CASA DE MACAU – July 2002 NEWSLETTER". www.casademacau.org. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ Lusa, Agência. "Portugal apela a estudantes portugueses em Hong Kong que enviem dados pessoais para receberem apoio". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Kristang, lost language of the Eurasians | Unravel Magazine". Unravel. 23 April 2018. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "About Kristang". Kodrah Kristang. 17 June 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Kodrah Kristang: The initiative to revitalize the Kristang language in Singapore".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "เกาะติดสถานการณ์ข่าว ข่าวด่วน ข่าววันนี้ ข่าวล่าสุด เนชั่นทีวี | เนชั่นออนไลน์". เนชั่นทีวี (in Thai). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Janjaem" (PDF).
- ^ ""มิตรคาม" ย่านวัดเขมรและวัดญวนสามเสนชุมชนริมแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยาที่ต้องถูกไล่รื้อ". Archived from the original on 15 July 2021.
- ^ "Luso-Asians and Macanese in Siam – Far East Currents". Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ Spirit of Asia : มะละกา และกุฏีจีน สายเลือดลูกผสมโปรตุเกส (15 เม.ย. 61), 15 April 2018, retrieved 31 March 2023
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "People of Lebanon".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Ancestry – ABS". Abs.gov.au.
- ^ "Portuguese Culture – Population Statistics". Cultural Atlas. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Cultural diversity: Census, 2021 | Australian Bureau of Statistics". www.abs.gov.au. 12 January 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ ""Autoridades australianas querem conhecer-nos mais e investir aqui"". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 15 March 2018. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "People of New Caledonia".
- ^ Glaser, Clive (2013), Morier-Genoud, Eric; Cahen, Michel (eds.), "The Making of a Portuguese Community in South Africa, 1900–1994", Imperial Migrations: Colonial Communities and Diaspora in the Portuguese World, London: Palgrave Macmillan UK, pp. 213–238, doi:10.1057/9781137265005_9, ISBN 978-1-137-26500-5, retrieved 1 April 2023
- ^ "People of Malawi".
- ^ "People of Zimbabwe".
- ^ "Portugueses no Zimbabué estão bem, diz ministro". BOM DIA (in Portuguese). 16 November 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "People of the DRC".
- ^ "Portugueses no Congo". 30 December 2018.
- ^ "People of Zambia".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "THE ORANGES OF PRESTER JOHN".
- ^ "Presença portuguesa na Etiópia sem registo de quaisquer mulheres". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 13 December 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "People of Senegal".
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Portugueses em Essuatini".
- ^ "Empresário português desaparecido desde domingo na Suazilândia". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 21 April 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "People of Tanzania".
- ^ "Ao sétimo país vive com 13 horas de luz todos os dias". Jornal Expresso (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "Observatório da Emigração". observatorioemigracao.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "Statistics Portugal – Web Portal". www.ine.pt. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Imigração sustenta subida da população em Portugal". www.cmjornal.pt (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Literatura portuguesa: origem, divisão, autores". Português (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "A língua de Camões – Ciberdúvidas da Língua Portuguesa". ciberduvidas.iscte-iul.pt. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Escritores e Literatura Portuguesa" (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Almeida Garrett: biografia, obras e estilo literários – Sua Pesquisa". www.suapesquisa.com. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Literatura Portuguesa. Origens da Literatura Portuguesa". Mundo Educação (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "As 20 obras mais importantes da literatura portuguesa". Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Expenditure in research and development activities (R&D) as a % of GDP: by sector of performance". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Portugal registers 7th largest increase in R&D investment since 2015". ANI. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ Mill, Hugh Robert (1896). "The Sixth International Geographical Congress, London, 1895. An uncommon original article from The British Association for The Advancement of Science report, 1895".
- ^ "introduçao". paginas.fe.up.pt. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ ONLINE, TUOI TRE (27 December 2019). "Chữ quốc ngữ những người đầu tiên khai sáng". TUOI TRE ONLINE (in Vietnamese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ Dutta, Soumitra; Lanvin, Bruno; Wunsch-Vincent, Sacha; León, Lorena Rivera; World Intellectual Property Organization (2022). Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 9789280534320. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ^ See the analysis of King, D.A., The scientific Impact of Nations – What difference countries for their research spending, Nature, vol. 430, 15 July 2004
- ^ (in Portuguese) Portugal é o país da UE onde despesa em investigação e desenvolvimento mais cresceu, Público (13 December 2008)
- ^ "Global Competitiveness Report 2020". World Economic Forum. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ ECO (25 March 2021). "Portugal é dos países mais dependentes das trocas comerciais intra-UE". ECO (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Exportações de serviços: total e por principais países parceiros comerciais". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Importações de bens: total e por principais países parceiros comerciais". www.pordata.pt. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ Machado, Alexandra. "Últimas notas de escudo podem ser trocadas até 28 de fevereiro de 2022". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ Bray, Chad (27 May 2014). "IntercontinentalExchange Set to Spin Off Euronext". DealBook. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Conservas A Ramirez, Portugal's oldest brand, opens nutrition center, Inside Portugal Travel, 2009". insideportugaltravel.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ "Testes PISA: Portugal supera média da OCDE". Visão (in Portuguese).
- ^ "E agora no PISA: alunos portugueses melhoram a ciências, leitura e matemática". Expresso (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 13 December 2018. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Management: The Portuguese who sit at the top of the world". Portugal Daily View. Archived from the original on 14 December 2017. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ "Erasmus decoded: Where do Europe's students go when they study abroad?". euronews. 7 March 2023. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ Directorate-General for Education, Youth (2022). Erasmus+ annual report 2021: statistical annex. LU: Publications Office of the European Union. doi:10.2766/63555. ISBN 978-92-76-58692-0.
- ^ autores, Vários; Carvalho, Bruno. Manual de Cozinha da Infanta D. Maria (in European Portuguese). Amass. Cook. ISBN 978-1-393-89909-9.
- ^ S.A, Priberam Informática. "Dicionário Priberam Online de Português Contemporâneo". Dicionário Priberam (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Ferrín, Xosé Luis Méndez (21 April 2014). "Broa". Faro de Vigo (in Spanish). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Pão e Produtos de Panificação". Produtos Tradicionais Portugueses (in Portuguese). Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Landgeist (25 June 2022). "Rice consumption in Europe". Landgeist. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Portugal e o arroz. 14 pratos a não perder (e onde os comer)". www.dn.pt (in European Portuguese). 9 September 2020. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Landgeist (21 December 2021). "Potato Consumption in Europe". Landgeist. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Livestock population in numbers". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "ANTÓNIO MARIA DE OLIVEIRA BELLO".
- ^ "Na Rota das Especiarias". 26 January 2024.
- ^ "Nando's restaurant numbers 2022". Statista. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Vinho Verde". Retrieved 10 February 2024.
- ^ "Louise Bourrat, uma Top Chef". Time Out Lisboa (in European Portuguese). 20 April 2023. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Um olhar sobre o cinema mudo em Portugal". Google Arts & Culture (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "| Cinema: Anthology of Film Archives featuring "The School of Reis" – NYCPortuguese American Journal". Portuguese American Journal. 20 June 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ Factos, Espalha- (21 November 2020). "15 séries e novelas que marcaram a televisão portuguesa". Espalha-Factos (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Os sinais do 'efeito- -telenovela'". 26 April 2006.
- ^ "Starngage: top 1,000 influencers in Portugal".
- ^ "Influencer Marketing Platform | Brinfer". brinfer.com. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "1000 Melhores Influenciadores do Instagram em Portugal | Ranking de Instagram do HypeAuditor". HypeAuditor.com (in Portuguese). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Instagram é a rede social mais utilizada pelos jovens em Portugal – Marketeer" (in European Portuguese). 27 September 2022. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ SAPO. "Facebook é a rede social mais usada em Portugal. Instagram, WhatsApp e TikTok estão a ganhar terreno". SAPO Tek (in Portuguese). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Top Social Media Statistics And Trends Of 2023 – Forbes Advisor". www.forbes.com. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Statista".
- ^ "Virginia Fonseca e Zé Felipe são tietados por fãs em Portugal; vídeo". GQ (in Brazilian Portuguese). 21 August 2022. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ a b "FOTOS – Giovanna Ewbank tem cidadania portuguesa, assim como Bruno Gagliasso e os 3 filhos do casal". www.purepeople.com.br (in Breton). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Coutinho consegue cidadania portuguesa e libera espaço para extracomunitário no Barcelona". ESPN.com (in Portuguese). 10 August 2018. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Brasileiro Felipe Neto criticado por festejar golo de Portugal: "Torcendo por colonizador"". www.ojogo.pt (in European Portuguese). 29 November 2022. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Flamengo no Brasil, Kelly Key revela seus times em Portugal e Angola". www.uol.com.br (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Pedro Scooby revela que conseguiu cidadania portuguesa para ficar perto dos filhos". Vogue (in Brazilian Portuguese). 23 September 2022. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Após polêmica sobre ensinar 'brasileiro' às crianças portuguesas, conteúdo de Luccas Neto será dublado com sotaque lusitano". O Globo (in Brazilian Portuguese). 22 December 2021. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Convocado por Tite, Ederson virou destaque em Portugal após dispensa no SP". www.uol.com.br (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Além dos Gagliasso, quem são os famosos que trocaran Brasil por Portugal; Ricardo Pereira e mulher recepcionam". Extra Online (in Brazilian Portuguese). 14 June 2021. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "GONOLIVIER". itsgonolivier.com. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ Hughes, Tobi (17 June 2021). "Digital content creator promotes Madeira". Madeira Island News Blog. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Quando o TikTok é palco do amor". Jornal SOL (in Portuguese). 15 February 2023. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "Biografia de Yasmine". MÚSICA DO GUETO (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ Pais, Tiago. "Odeith, o artista português que faz o graffiti saltar do muro". Observador (in European Portuguese). Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ^ "FANNY RODRIGUES".
- ^ "Abril 2020 – GALERIA DOS GOESES ILUSTRES". galeriadosgoesesilustres.blogs.sapo.pt. Retrieved 7 June 2023.
- ^ "discoverazores.org". www.discoverazores.org. Archived from the original on 20 June 2023. Retrieved 7 June 2023.











